Automation and AI, working as transformative force for India’s MSMEs
By Staff Report May 26, 2025 1:00 pm IST
Indian small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in manufacturing face growing pressure to stay competitive amid global challenges and the rise of automation.
The Competitiveness Imperative for SMEs
India’s small and medium manufacturing businesses face a decision: use automation and AI or risk falling behind. These businesses are crucial for India’s industrial production but face challenges. Global supply chain issues and higher quality standards are making old work methods difficult. Fewer skilled workers are available because younger people prefer office jobs, leaving factories with a skills gap. SMEs compete with large global companies that use advanced technology. Using automation and AI is essential for survival and growth. Industry 4.0 technologies don’t need a lot of money.
Unlike the past, which required buying machines, today’s SMEs can add sensors to existing equipment and connect them to systems at a lower cost. Advances in robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and AI allow factories to upgrade. Companies act early and gain an advantage, while those that wait may fall behind. Automation and AI are key to staying competitive by increasing productivity, ensuring quality, and meeting the demands of local and export markets.
Benefits of Automation and AI for SMEs
- Productivity and Efficiency: Automation cuts down on manual work and waiting time. Some small engineering companies have used digital tools to increase productivity. AI tools find problem areas and make work processes smoother, leading to an increase in efficiency each year.
- Cost Savings: SMEs save money by reducing mistakes, waste, and downtime. Unplanned machine breakdowns can make up a quarter of production costs. IoT sensors help by predicting problems and fixing them early. Automation reduces labour costs by performing tasks.
- Improved Quality: Consistency rises when machines and AI assist in production. Computer vision systems inspect products in real-time, catching defects and ensuring parts meet specifications.
- Faster Response and Lead Times: Digital tools and AI help speed up decisions. An AI like ChatGPT can create quotes or answer customer questions. Faster quotes and order processing increase business and allow earlier delivery.
- Workforce Enablement and Safety: Automation handles jobs. This helps reduce accidents and tiredness. Workers can learn new skills to manage machines and do tasks like improving quality or programming.
- Manufacturers around the world use AI solutions. In India, investments in new technology have paid off by reducing downtime and increasing production. The message for small and medium businesses: using automation and AI can improve productivity, reduce costs, enhance quality, and increase flexibility.
10 Low-Cost Automation Ideas for Indian SMEs
Small businesses can use solutions under ₹10 lakh. They can upgrade machines or add digital tools.
1. Predictive Maintenance Sensors (CNC Machines): Install vibration and temperature sensors on CNC machines. These send data about spindle vibration or tool wear to a dashboard. If something unusual is detected, maintenance can be planned early. Estimated cost: ₹2–5 lakh. Benefit: Prevent breakdowns and reduce downtime.

2. Load Monitoring on Legacy Machines (Lathes/Presses): Upgrade lathe machines or presses with load cells or motor current sensors. These check the force and send an alert if limits are exceeded. Cost: ₹50,000–2 lakh. Benefit: Stop tool damage or overloads, helping equipment last and keeping product quality.
3. AI-Powered Quotation Assistant: Use a tool like ChatGPT to automate sales quotes. Train it with past quotes, product info, and pricing rules. Cost: ₹0.5–1 lakh. Benefit: Speeds up sending quotes, increasing order chances.
4. Machine Vision for Quality Inspection: Set up a camera and AI software at an inspection spot. A camera on a line can find product defects using image recognition. Cost: ₹3–6 lakh. Benefit: 100% inspection coverage without more workers.
5. Smart Energy Meters and Controls: Install monitors on machines to track electricity use. These can put machines on standby or balance the load. Cost: ₹1–3 lakh. Benefit: Reduces energy use and bills.
6. Collaborative Robots (Cobots) for Material Handling: Use a robotic arm or cobot for jobs like moving parts or packing. Cost: ₹8–10 lakh. Benefit: Cobots work with people and handle tasks.

7. Automated Conveyor or Feeder Systems: Use a conveyor belt or feeder to connect processes. For example, move parts from a drilling to a tapping station. Cost: ₹4–10 lakh. Benefit: Removes handling delays and reduces labour.
8. Simple PLC/Arduino-Based Controllers: Automate tasks using a PLC or Arduino. For example, automate dip and lift in a paint shop. Cost: ₹1–2 lakh. Benefit: Replaces manual tasks with control.
9. Digital Performance Dashboard: Use sensors or counters to send data to a dashboard or sheet. Display data on the shop floor. Cost: ₹1–3 lakh. Benefit: Enhances transparency and responsiveness.
10. Environmental Sensors and Safety Alerts: Use sensors to detect temperature, humidity, gas leaks, and smoke. Install light curtains or sensors on machinery. Cost: ₹50,000–1 lakh per upgrade. Benefit: Prevents accidents and ensures conditions.
Summary of 10 Low-Cost Automation Ideas (Under ₹10 Lakh):
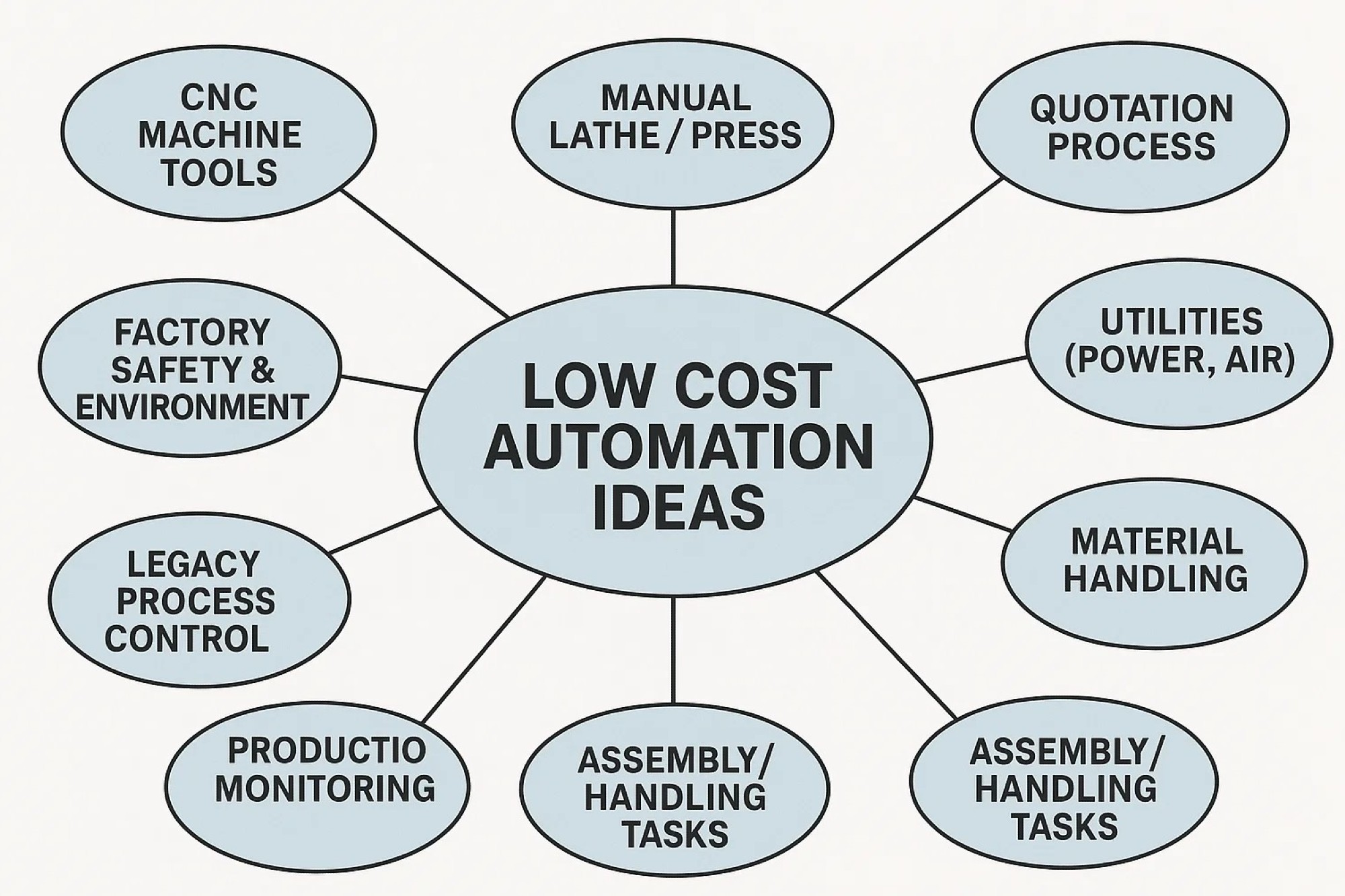
| Machinery/Process | Automation Type | Est. Cost (₹) | Key Benefits |
| CNC machine tools | Vibration/temperature IoT sensors for predictive maintenance | 2–5 lakh | Early fault detection; reduce breakdowns and downtime. Improve machine availability. |
| Manual lathe / press | Load sensor and cutoff/alarm | 0.5–2 lakh | Prevent overload & tool breakage; maintain product quality consistency. |
| Quotation process | ChatGPT-based AI quoting assistant | ~1 lakh | Instant quote generation; cut lead time, improve response to customers. |
| Quality inspection | AI machine vision camera system | 3–6 lakh | Automated 100% inspection; catch defects humans miss, ensure high quality. |
| Utilities (power, air) | Smart energy meters & IoT controls | 1–3 lakh | Optimize energy use; lower electricity costs, detect inefficiencies. |
| Material handling | Small conveyor or feeder mechanism | 4–10 lakh | Reduce manual transfer; faster throughput, more ergonomic workflow. |
| Assembly/handling tasks | Low-cost collaborative robot (cobot) | 8–10 lakh | Automate repetitive tasks; increase output hours, improve safety. |
| Legacy process control | Microcontroller/PLC automation kit | 1–2 lakh | Automate manual operations; improve consistency and free up labor. |
| Production monitoring | Digital dashboard (sensors + display) | 1–3 lakh | Real-time output tracking; quick issue identification, 40–70% productivity gains seen. |
| Factory safety & environment | Safety sensors (temperature, gas, light curtains) | 0.5–1 lakh | Prevent accidents; maintain optimal conditions for quality and compliance. |
Real-World Examples of Transformation
To understand how these ideas play out, consider a few scenarios drawn from actual SMEs implementing automation:
- CNC Machine Health Monitoring: A precision parts manufacturer located in Pune implemented retrofitted vibration sensors on its CNC milling machines. The sensor data identified a spike in the spindle of one machine. The maintenance team intervened and identified a bearing fault, which they rectified during a scheduled weekend. By addressing the issue, the company averted a breakdown that could have disrupted production. Machine uptime increased by 15%, and the firm saved ₹5 lakh in downtime losses over one year. Predictive maintenance through the Internet of Things (IoT) has become their practice.
- Lathe Machine Load Sensing: An automotive components SME in Coimbatore implemented load cells on its manual lathes. In instances where the cutting force increased, such as from a dull tool or incorrect feed rate, the system issued an alert and disconnected the power supply. Operators adjusted the tool and resumed operations. Tool breakages were reduced, and the rate of product rejection decreased by 20%. The investment of ₹1 lakh per machine was recouped through savings in tooling and scrap costs.
- AI-Based Quotation System: In a fabrication workshop located in Delhi, quotation delays were due to manual calculations by engineers. The workshop implemented a ChatGPT-based quotation assistant, integrated with their pricing database. Upon receiving an inquiry, the salesperson inputs specifications into the AI tool. The system generates a quotation detailing materials, labour, and delivery timelines. The average time to produce a quotation decreased from 3–4 days to less than one day. The workshop experienced a 15% increase in order conversions.
- Quality Control with Machine Vision: An electronics assembly unit in Bengaluru producing wiring harnesses faced challenges in manual visual inspection. The company implemented a machine vision station. Each harness is placed under a camera that verifies colour coding and connection. Deviations trigger an alert for rework. The defect escape rate was reduced. Inspectors were reassigned to upstream checks and final testing. The SME reported a reduction in customer complaints and secured additional orders.
- These instances show that SMEs can realise benefits through targeted automation. Each solution was implemented with a financial outlay and without an overhaul of the operation.
Trends Driving the Automation Wave
Several trends are pushing Indian SMEs toward automation and AI adoption:
- Labour Shortages and Rising Skill Requirements: Manufacturers encounter difficulties in recruiting operators and technicians. Automation performs repetitive tasks. Enhancing digital competencies is required to fulfil new roles. Skill development initiatives address labour shortages.
- Export Opportunities and Global Competition: The “China + 1” strategy prompts corporations to seek suppliers beyond China. SMEs must adhere to international standards. Adoption of digitisation enhances competitiveness. Industry forecasts indicate an 8–10% annual growth rate in the SME sector. Automation supports consistency and scale.
- Customer Demand for Quality and Speed: OEMs and consumers demand quality and delivery. Automation addresses these needs. AI ensures defect-free products. Robotics enables faster production. Data-driven processes support demand changes.
- Falling Technology Costs: Costs of sensors, controllers, and computing have decreased. A factory with 50 employees can implement technologies. Open-source software and cloud services reduce barriers. Plug-and-play devices allow quicker installations.
- Supportive Ecosystem and Government Push: Government programmes like Make in India and PLI support modernisation. There is a network of automation vendors, solution providers, and incubators. Collaboration among technology providers, institutions, and SMEs is increasing.
These trends indicate that SME automation is timely. Adoption can improve competitiveness.
Getting Started: A Roadmap for SMEs
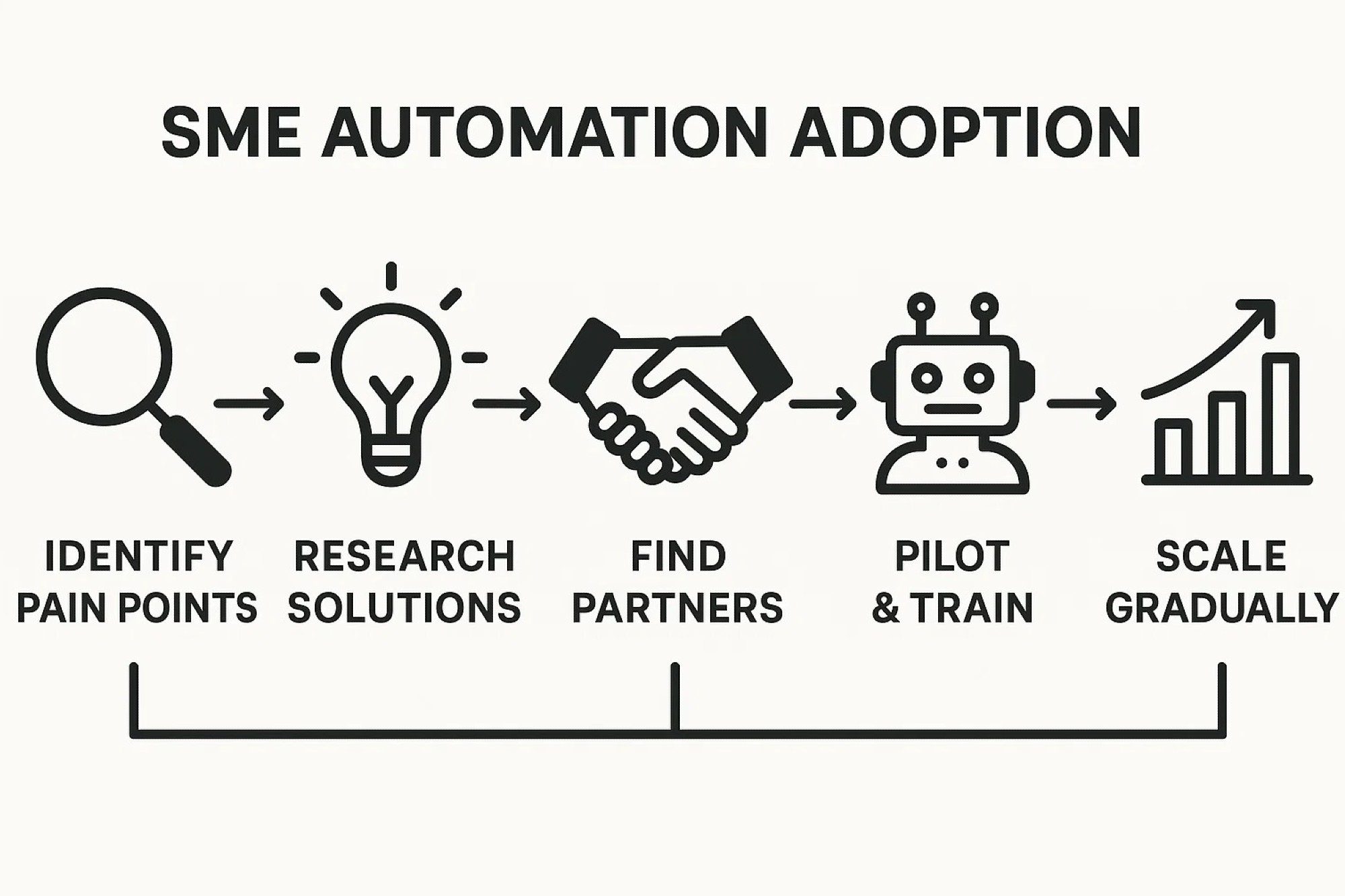
- Identify Pain Points: Map processes to identify repetitive, labour-intensive, or error-prone tasks. Prioritise areas such as maintenance, inspection, or order processing.
- Research Low-Cost Solutions: Examine the list of ten ideas for alignment with needs. Use products or kits from suppliers or marketplaces. Plan for add-ons instead of new machines.
- Find Local Integrators or Partners: Use industrial automation integrators. Innovation hubs and incubators help connect SMEs with providers. Consultation can provide an implementation path.
- Pilot and Train: Implement a solution on a limited scale. Evaluate outcomes. Train staff with sessions or short courses.
- Scale Up Gradually: If the pilot is successful, plan to expand. Use insights to improve methods. Reinvest savings into automation. Early successes can support broader adoption.
- Leverage Government and Industry Programs: If the pilot succeeds, create a strategic plan to expand. Use insights to refine the methodology. Reinvest cost savings. Early successes build confidence and support further efforts.
- Collaborate and Network: Learn from peers. Use associations or forums to find examples. Collaborate with startups or students for prototypes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future
Automation and AI are changing manufacturing worldwide. Indian small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) need to keep up. This change is important to stay competitive. It helps with productivity, cost, quality, and speed, which are key to success today. This technology is affordable. Even with budgets, SMEs can make upgrades that bring benefits. According to McKinsey, Industry 4.0 lets companies connect machines to digital systems for improvements at a cost. Indian manufacturing SMEs are at the start of an era. Those that innovate by using sensors, algorithms, and training will do well.
They will find export opportunities, meet standards, and run operations. There is support, like government incentives and tech partners, to help them. Now is the time to act. By adopting automation and AI, Indian SMEs can secure their future and boost the country’s manufacturing growth. Future factories are not just plants. They can also be workshops across India, using technology to compete. Automation and AI are the tools, that SME leaders need to use to build industries.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.