Safran deepens aerospace roots in India
By Staff Report September 1, 2025 7:40 pm IST
Safran is an international high-technology group, operating in the aviation (propulsion, equipment and interiors), defence and space markets. Its core purpose is to contribute to a safer, more sustainable world, where air transport is more environmentally friendly, comfortable and accessible. Jetendra Gavankar, CEO and Country Head for Safran India, discusses the company’s significant and ongoing expansion within India’s aerospace and defence sectors.
Can you provide an overview of Safran’s current manufacturing footprint in India, including the number of facilities, their locations, and primary functions?
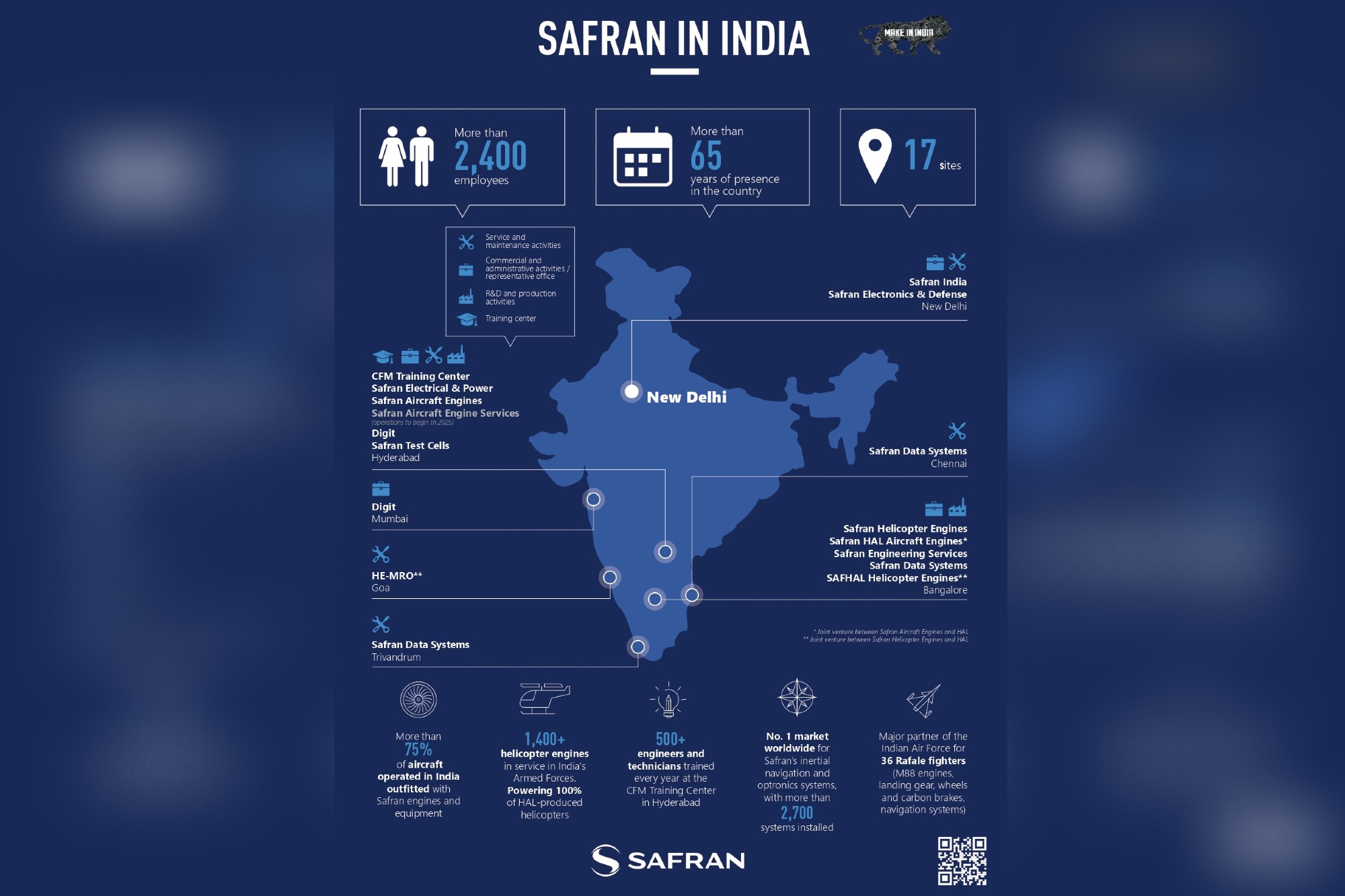
Safran has significantly expanded its footprint in India, establishing itself as a key partner in the nation’s aerospace and defence ecosystem. As of 2025, Safran operates multiple production, MRO, Engineering and R&D sites across Hyderabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Trivandrum, Mumbai and Goa, with a new state-of-the-art facility for LEAP engine maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) set to open in Hyderabad. Our new electronics manufacturing facility and a 3,000-square-meter R&D centre in Bengaluru are expected to employ hundreds and drive innovation in avionics and defence computing systems. Our workforce in India exceeds 2,400 employees, and we also collaborate with major Indian organisations, including HAL, BEL, DRDO, ISRO, and many new space companies. Our investments, exceeding several million USDs since 2018, align with the nation’s “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives, supporting local manufacturing, technology transfer, and skill development. The recent inauguration of a second office in New Delhi further strengthens our operational and collaborative presence in both civil and military aviation sectors. The footprints are elaborated below in the Infographic.
How do you ensure that your Indian manufacturing facilities meet global standards for quality and technology?
Safran has facilities in India, which are either its direct subsidiary or joint ventures. In both such setups, we ensure that our manufacturing facilities meet global standards in quality and technology by directly transferring best practices and advanced technologies from our international operations to several of our manufacturing facilities at 17 Indian sites. These facilities incorporate cutting-edge manufacturing processes, such as Industry 4.0 automation, IoT-enabled monitoring, and data analytics, aligning them with the technological sophistication of our global plants. We also implement our global Quality Management System (QMS) across Indian operations and suppliers, ensuring consistency and integration into the international supply chain.
Safran conforms to the standards and certifications of the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), which in turn enables us to focus on EASA’s needs in terms of quality, sustainability, and process.
Additionally, we invest in local talent development by training Indian employees at global centres and nourishing partnerships with Indian companies and research organisations. Safran ensures sustainability through energy-efficient systems and green building standards at its Indian sites. This dual focus on global competitiveness and local alignment allows Safran India to deliver world-class aerospace products while supporting the “Make in India” initiative. We also follow “Aero Excellence”, a universal standard for operational excellence designed for suppliers to the aerospace, space, and defence industries, which helps accelerate industrial maturity. The “Aero Excellence” program aims to enhance supply chain resilience and industrial competitiveness. Open to all industry stakeholders, Aero Excellence is part of an innovative and global approach towards continuous improvement of industrial performance.
What are some of the biggest challenges you face in manufacturing aerospace-grade components in India, and how do you overcome them?
Major challenges in manufacturing aerospace-grade components in India include infrastructure-related challenges, non-availability of local sources for raw materials, regulatory complexities, and a shortage of skilled labour. To overcome these, the government is streamlining certification processes, incentivising R&D, and promoting local sourcing of materials. The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and automated tools like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, is continually improving production efficiency and reducing costs. Collaborative efforts between government, industry, and academia are enhancing skill development and fostering innovation, while MSME involvement and public-private partnerships are expanding the ecosystem and global competitiveness. We are sure that by 2030, India will have a very mature aerospace manufacturing ecosystem.
What role do Safran’s Indian facilities play in the production and support of the LEAP engine?
Our Indian facilities play a crucial role in the global production ecosystem of LEAP engines (developed by CFM International: a joint venture between Safran Aircraft Engines and GE Aerospace). Our facilities in Hyderabad and Bangalore contribute significantly to the manufacturing of key components, including rotating parts, seals, pipes and wire harnesses. These facilities support advanced machining, assembly, and quality assurance, aligning with global standards. The India operations enhance production capacity and reinforce our commitment to Make in India for the world, skill development, and technology transfer, making them an integral part of the LEAP engine’s global supply chain and long-term sustainability.
Can you elaborate on Safran’s collaborations with Indian partners, such as Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), in manufacturing endeavours?
Safran India has established multiple strategic collaborations with Indian partners, notably HAL, BEL, and various MSMEs, strengthening India’s aerospace and defence ecosystem. With HAL, we have a decades-long partnership, co-developing the Shakti helicopter engine and now jointly designing and producing the new-generation ‘Aravalli’ engine for the Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH) and Deck-Based Multi-Role Helicopter (DBMRH). We have also signed agreements for manufacturing LEAP engine components (for exports).
With BEL, we are establishing a joint venture to manufacture, customise, and maintain the HAMMER precision-guided weapon in India, including the establishment of a Centre of Excellence for technology transfer and advanced manufacturing. We have also transferred technology for manufacturing Inertial Navigation Systems for aircraft and ships to Indian DPSUs and DRDO. We are also collaborating with several Indian MSMEs, integrating them into our supply chain and fostering technology transfer, thus boosting local industry participation and positioning India as a global aerospace hub.
What advancements have been implemented in Safran’s Indian manufacturing facilities to enhance efficiency and sustainability?
We have significantly advanced sustainability and efficiency in India’s aerospace sector through multiple initiatives. We have invested several million USD to establish state-of-the-art manufacturing and Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) facilities in Hyderabad. They apply global standards for energy efficiency, automation, and green building practices, including extensive use of solar power. Our Hyderabad plant for LEAP engine parts utilises Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT-enabled monitoring and data analytics, to enhance operational efficiency and minimise environmental impact.
Safran has also contributed to environmental programs, such as ‘Namami Gange’, and actively reduces its carbon footprint by adopting eco-friendly manufacturing practices and supporting community-based sustainability projects.
How does Safran integrate Indian talent into its global supply chain, and what training programs are in place to support this?
Safran India is actively fostering the growth of Indian MSMEs, startups, and industries by integrating them into global aerospace, defence, and software supply chains. Through strategic partnerships, technology sharing, and capability development initiatives, we support Indian suppliers in meeting stringent international quality and certification standards. We regularly conduct supplier development programs, technical workshops, and audits to help local vendors scale up their capabilities. Our strong presence in India, including R&D, manufacturing, and engineering facilities, creates long-term business opportunities for local firms. The group also collaborates with startups and software companies on innovation, digitalisation, and advanced analytics. We are committed to the “Make in India” initiative, sourcing increasingly from Indian partners and promoting indigenisation. This ecosystem-building approach is enabling Indian companies to serve local needs while also exporting high-quality components and services to global markets. Safran will soon be conducting a “Suppliers Meet” in Bangalore to connect with new potential suppliers and to enhance sourcing from existing suppliers.
Can you discuss Safran’s involvement in India’s space sector and the manufacturing contributions supporting this domain?
We are present in Space Equipment supplies for both ground segments and onboard satellites, as well as for the Space Surveillance segment in India, working alongside both government and private industries.
ISRO and CNES have a rich history of cooperation and collaboration spanning around six decades. The cooperation began with the establishment of sounding rocket launching facilities at Thumba in the early 1960s. It progressed to various areas of space activities in the years that followed. Safran also has a long-standing partnership with Indian agencies, such as ISRO, and private sector players, contributing to major national missions, including the Chandrayaan moon mission, Mars Orbiter Mission, and Gagan-Yaan human spaceflight project, as well as India’s moon mission.
Manufacturing is a key focus for us in India’s space sector, and we are actively supporting the “Make in India” initiative by developing local industrial capabilities and transferring advanced technologies. In India, Safran Space remains committed to the vision of Make in India for India, and for the rest of the World within the frame of its Atma-Nirbhar Bharat mission, through a local entity called Safran Data Systems India. As a fact, SDS India recently reached a new milestone in its “Make in India” journey – they just delivered four of our first Made in India CORTEX – telemetry and telecommand units, to the Department of Space. Safran Data Systems India (SDSI), which was established after acquiring Captronics Systems, is deeply involved in designing simulation systems for Avionics, electronic warfare missions for DRDO and HAL, automated testing equipment for integrating and verifying rocket and spacecraft components, and supporting launch testing for ISRO.
We have collaborated with educational institutions like IIT Tirupati, nominated by DST for Position & Precision Navigation Technology, establishing a Safran Lab with a GNSS simulator donated by Safran4D.
What are the plans for expanding Safran India’s manufacturing capabilities in India?
We are accelerating our expansion in the aerospace, defence, electronics, and space sectors, guided by a comprehensive vision for the next decade:
First, we are focusing on industrial growth and MRO operations. Safran is establishing a facility in Hyderabad for LEAP engine maintenance, repair, and overhaul, which is expected to be operational by the end of 2025. This will bring the total number of production and MRO sites to six across Hyderabad, Bangalore, and Goa.
Second, we are investing in electronics and R&D by launching a new electronics design and manufacturing plant in Bengaluru, covering 12,000 square meters and employing approximately 400 staff. The facility will produce avionics, defence electronics, and calculators, with operations commencing in 2026. Third, Safran is strengthening strategic partnerships with BEL and HAL to localise smart munitions (HAMMER), establish a Centre of Excellence, and collaborate with HAL to co-develop a new generation helicopter engine for the IMRH program. In the space sector, Safran Data Systems India (SDSI) will continue to support ISRO missions, the private space sector, and India’s growing demand for space situational awareness, to double our presence in this segment. Safran is committed to the ‘Make in India ‘ initiative by sourcing a significant portion of its products and services locally.
Safran has integrated India into its aerospace and defence (A&D) export strategy.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.