Fronius, the Austrian technology company, marks 80 years of innovation in welding and solar energy, evolving from a small repair shop to a global industry leader.
Fronius, a family-owned technology company headquartered in Austria, celebrates its 80th anniversary this year. What began in 1945 as a small regional repair shop has grown into a global enterprise known for its pioneering solutions in welding technology, solar energy, and battery charging systems.
The company was founded by electrical engineer Günter Fronius on June 20, 1945. Operating from a hotel, he began offering repair services for radios and electrical appliances. Recognising a growing need, he soon developed a device to recharge car batteries—marking the company’s first product and the beginning of a legacy of innovation.
“Our roots are built on resourcefulness, collaboration, and a bold approach to innovation,” said CEO Elisabeth Engelbrechtsmüller-Strauß, granddaughter of the founder. “In post-war Austria, resources were limited, but that only strengthened my grandfather’s determination to create practical and affordable solutions for everyday needs.”
From Welding to Solar: A Legacy of Expansion
In 1950, Fronius expanded its offerings to include welding transformers, a move that would shape its long-term growth as an industrial company. A new chapter began in 1980, when the second generation—Brigitte Strauß and Klaus Fronius—took over leadership and began international expansion. Today, Fronius operates 37 subsidiaries around the world.
The company entered the solar energy space in 1992, long before it became a mainstream solution. “Our commitment to renewable energy drives us to develop integrated systems that connect electricity, heating, cooling, and mobility to realise our vision of ‘24 hours of sun’,” added Engelbrechtsmüller-Strauß, who has led the company since 2012.
Driving Industry Innovation Worldwide
Fronius has consistently contributed to industrial advancement, particularly in automotive manufacturing. A major innovation was the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) welding process, introduced 20 years ago. CMT enabled the thermal joining of materials like galvanised steel and ultra-thin aluminium sheets, marking a turning point in welding technology.
The company currently focuses on two key business areas:
With a global workforce of 7,000 employees, Fronius remains dedicated to its founding mission: mastering and managing electricity as a key energy source of the future. “Our goal is to create a sustainable future for current and future generations,” Engelbrechtsmüller-Strauß stated.
Committed to a Sustainable and Independent Future
As Fronius celebrates this milestone, it continues to look forward. The company remains focused on advancing energy conversion technologies and upholding its values of financial independence, high-quality engineering, and European manufacturing.
“We can’t predict the future,” said Engelbrechtsmüller-Strauß, “but we’re committed to remaining independent and strengthening Austria’s position as a centre for innovation. Research and quality will always be at the heart of what we do.”
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Lauritz Knudsen introduces its largest product portfolio to boost automation and energy efficiency across India’s industrial hubs, aligning with the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
Lauritz Knudsen Electrical and Automation today announced the launch of its most extensive product line, aimed at India’s key industrial clusters and economic corridors. As part of the programme, the business will visit 30 industrial locations around the country to promote technology adoption in the core manufacturing and infrastructure industries.
The new portfolio focuses on low-voltage electrical solutions, industrial automation systems, and technology for the future energy landscape. The effort aligns with the Government of India’s Viksit Bharat 2047 goal of creating a technologically advanced, energy-efficient, and economically resilient nation.
Naresh Kumar, COO of Lauritz Knudsen Electrical and Automation, stated, “At Lauritz Knudsen, our mission is to deliver smart technologies that help customers work safer, faster, and smarter. With India’s electrical sector set to surpass USD 95 billion by 2029 and industrial automation reaching USD 39.65 billion by 2033, our new portfolio reinforces our commitment to accessible, adaptable innovation that powers India’s smart, clean, and future-ready growth.”
Key launch highlights
Lauritz Knudsen’s solutions are developed with a thorough understanding of India’s regional diversity, policy framework, and sector-specific requirements. The ongoing city trip includes Pune, Noida, Bhubaneswar, Coimbatore, Guwahati, and other promising industrial hubs.
Through direct contacts with system integrators, engineers, contractors, policymakers, and industry leaders, Lauritz Knudsen demonstrates its commitment to India’s sustainable and technology-driven future.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
IDEX continues to lead with resilient strategies and smart innovation. Vikas Kaushik, Vice President – FMT Pumps, India, discusses how the company leverages decentralised operations, digital tools like Cognito, and region-focused agility to meet the demands of a borderless manufacturing landscape.
How has globalisation influenced the operations of manufacturers, and what challenges do they face in borderless trade?
Globalisation has enabled producers such as IDEX to access varied markets, build innovation on a worldwide scale, and localise product development, as we did for Cognito EODD pumps. Yet, borderless trade poses challenges in terms of geopolitical volatility, changing trade policies, and supply chain risks. Resilience is required in overcoming these.
Our decentralised approach enables each business unit to remain local to customer requirements, while pooled technological know-how delivers operational excellence. Ensuring product conformity across borders, handling logistics during global disruption, and ensuring supply continuity are among the main areas of focus.
We also observe localisation for local markets as a vital supplement to globalisation. At IDEX, we counter risks by making strategic regional investments, customer-centric innovation, and digital integration across operations to remain nimble in an economy with no borders.
How have supply chain disruptions (pandemic, semiconductor shortages, logistics crises) changed the supply chain strategies around the world? Does it vary with changing geography?
The pandemic and other bottlenecks have led manufacturers to prioritise resilience over cost-effectiveness. At IDEX, we maximise the local supply chain and incorporate intelligent technologies such as COGNITOsmartINSIGHTS to remotely monitor equipment, predict maintenance, and maintain uptime. Geography is critical supply strategies in India, for instance, prioritise local sourcing and rapid execution, whereas established markets emphasise automation and data analysis.
Our solution is to create flexibility within sourcing and manufacturing, to regionalise production footprints, and to facilitate digital transparency along the value chain. This allows us to counter region-specific disruptions while ensuring global standards. In the end, resilience, visibility, and responsiveness now characterise supply chain strategy regardless of geography.
How are companies integrating sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance into their global operations?
Sustainability and ESG form the core of IDEX’s innovation strategy. Our Cognito EODD pumps, for example, save up to 70% energy compared to standard AODD pumps, substantially reducing power consumption and carbon footprints. We focus on robust, repairable design to eliminate waste and minimise material usage.
IoT integration via COGNITOsmartINSIGHTS facilitates predictive maintenance, avoiding unplanned downtime and resource wastage. Wherever we operate, we follow responsible sourcing practices and focus on ethical governance. Regionally, we adapt our ESG strategy to regulations and social requirements. From minimising lifecycle environmental footprints to facilitating energy efficiency and safe operations, our product and operational choices align with ESG principles, giving value to stakeholders while driving global sustainability objectives.
Is the future of global manufacturers moving towards a “One World, One Market” approach, or are we seeing a more fragmented market structure?
The dream of ‘One World, One Market’ is transforming into a balanced strategy where global connectivity is combined with local specificity. Our business strategy integrates global R&D and design quality with local engineering and customisation.
This hybrid model enables us to stay responsive and relevant in different markets. Instead of fragmentation or homogenisation, the future lies in dynamic regional ecosystems supported by global integration and digital intelligence. Cognito a revolutionary innovation is rapidly making its mark on the global stage by solving major industry pain points.
Recognised as the most innovative and energy-efficient product by customers and industry leaders, Cognito is helping businesses save energy, reduce their carbon footprint, and achieve faster ROI. As Cognito drives a more sustainable future, our dedicated team across the world is reaching markets and sharing success across borders.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
EMO Hannover 2025 highlights sustainable solutions from leading manufacturers, focusing on resource efficiency, emissions reduction, and circular production.
Sustainability will be a core theme at EMO Hannover 2025, with exhibitors demonstrating resource-efficient production methods, emissions reduction plans, and circular economy concepts. These programmes protect the environment and the climate, help firms remain competitive, and support their obligations to future generations.
Promoting Carbon Footprint Transparency
Ceratizit Deutschland GmbH is taking focused initiatives to reduce CO₂ emissions throughout its value chain. A significant component is a proprietary recycling technique that allows for the recovery of raw materials from secondary sources, lowering the product’s carbon footprint (PCF).
Dr Andreas Lackner, our chief executive officer, commented, “Our aim is to establish a common standard for calculating and classifying the carbon footprint of cutting tools, hard material solutions, and carbide powders. Ceratizit created a PCF model that contributed to VDMA standard sheet 35111, which is now used as an industry reference.”
A milling cutter line constructed from 99% recovered carbide offers up to 30% greater performance and the lowest CO₂ emissions in its class.
Practical Sustainable Measures
Ingersoll Werkzeuge GmbH, situated in Haiger, has undertaken several sustainability efforts, including eco-friendly packaging, regrinding services to extend tool life, and a photovoltaic system generating 700,000 kWh yearly, saving around 184 tonnes of CO₂.

Leon Pulverich, Environmental and Energy Management Officer, stated, “We have taken various measures to reduce our ecological footprint while remaining economically efficient. When selecting new machines, the corporation prioritises energy efficiency in order to cut consumption and operating expenses.”
Developing Tools for a Greener Future

Mapal Dr. Kress SE & Co. KG specialises in sustainable tool design. Combination tools reduce tool changes and machine run times, resulting in energy savings. MQL-compatible tools reduce coolant usage and disposal expenses. Replacement head systems and reconditioned tools help to prevent material waste.
According to Jacek Kruczynski, chief technology officer, “Sustainability is not a foreign concept at Mapal but an absolute matter of course in our ideas and developments. The award-winning Uniq hydraulic chuck has a tenfold service life and uses less energy than standard alternatives.
Optimising Machines for Efficiency
Kapp Niles GmbH & Co. KG has updated its grinding machines to improve energy and material efficiency. FEM-based component design, frequency-controlled pumps, and electronic systems have replaced traditional hydraulic systems, resulting in significantly lower energy use.

Additive manufacture of coolant nozzles increased efficiency by 60%, and mineral cast machine beds reduced CO₂ emissions. Intelligent shut-off functions and pressure-reduction technologies further cut power and air consumption.
Ralf Dremel, Head of Product Management, stated, “The EU Ecodesign Regulation presents new challenges and opportunities for innovation. We see our internal sustainability goals as a way to secure future competitive advantages.”
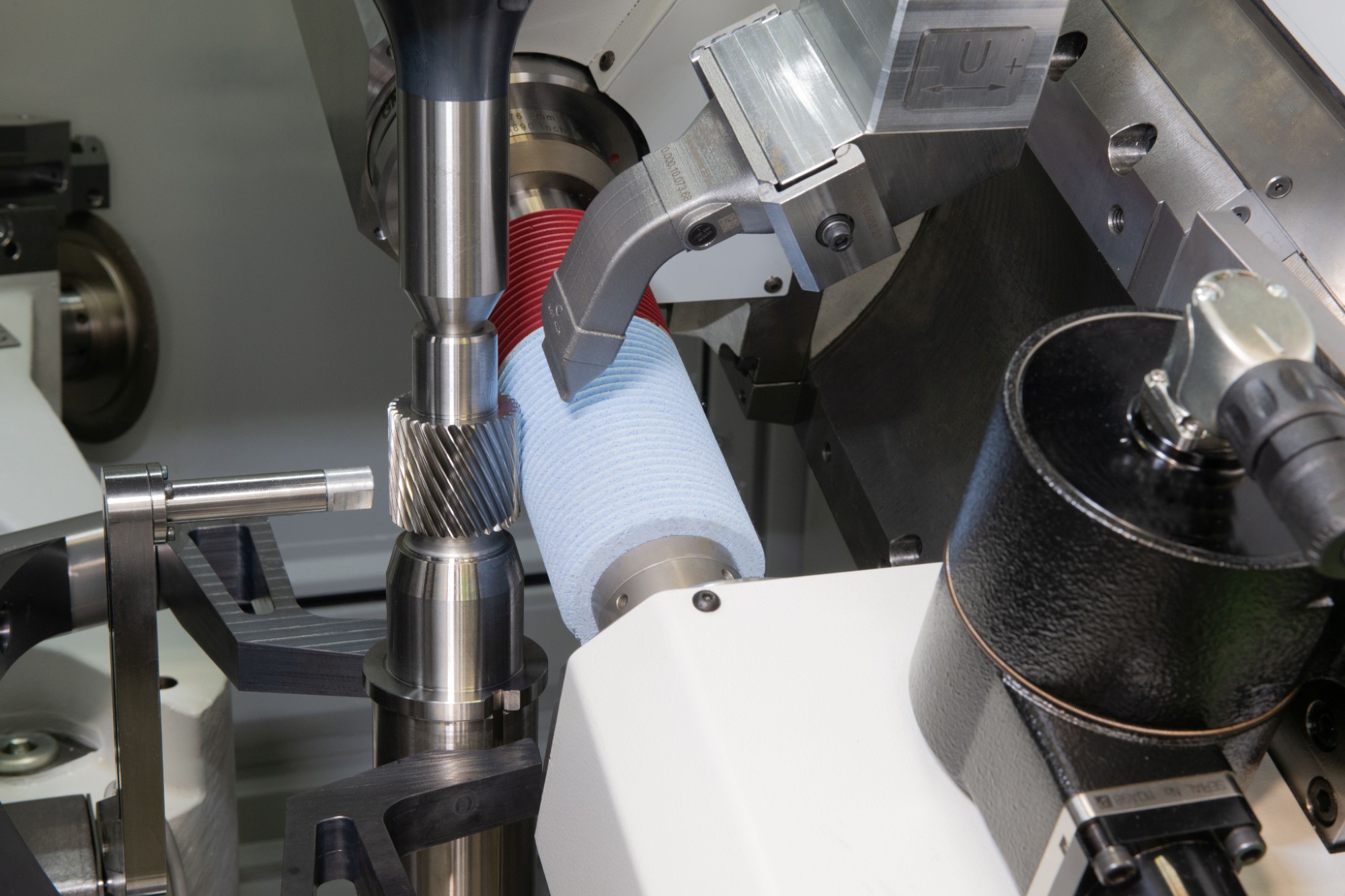

EMO Hannover 2025 highlights sustainability, automation, and digitalisation as major themes for the future of manufacturing. Visitors will see innovative solutions and interact with global industry leaders driving transformation.
For more information, visit www.emo-hannover.de.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Honeywell has introduced new AI tools to strengthen industrial cybersecurity and support safer, more resilient operations.
Honeywell introduced new AI-enabled digital technologies at the 49th annual Honeywell Users Group (HUG) to expedite the shift from industrial automation to autonomous systems. Honeywell launched two cybersecurity solutions, Honeywell Cyber Proactive Defence and Honeywell OT Security Operations Centre, and enhanced its Digital Prime platform to improve operational efficiency and system resiliency.
Honeywell Cyber Proactive Defence uses AI and behavioural analytics to detect anomalies in OT environments. It establishes a baseline for system operations, provides actionable insights, and employs deception techniques to divert attackers away from critical assets.
The Honeywell OT Security Operations Centre is a vendor-neutral, agentless solution that provides 24/7 monitoring for early signals of cyber threats in OT systems. It incorporates on-site incident management and provides a comprehensive overview of the cyber threat landscape.
Honeywell improved the Digital Prime Ecosystem by uniting three services Solution Enhancement Support Program (SESP), Enabled Services, and Assurance 360 on a single platform. It allows businesses to test and adjust engineering projects before deployment, reducing downtime and increasing throughput while providing near-real-time performance information.
According to a Honeywell poll of 300 U.S. decision-makers in energy and related sectors, 91% believe AI has near-term potential to improve energy security, and 85% are either employing or testing AI.
Pramesh Maheshwari, President of Honeywell Process Solutions, stated, Industries are looking for AI-enabled, enterprise-wide solutions that can adapt and make decisions in dynamic environments, and our new digital technologies help them develop safer, more dependable, and efficient operations. As we guide our customers on the path from automation to autonomy, Honeywell’s domain expertise is poised to help them rethink how they use technology to drive innovation and gain a competitive edge.”
Availability
Honeywell Cyber Proactive Defence and the OT Security Operations Centre are now available internationally. The expanded Honeywell Digital Prime Ecosystem will be available in Q4 2025.
For more information, visit www.honeywell.com.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Gujarat introduces the Electronics Component Manufacturing Policy-2025 to attract investments, boost local production, and offer dual incentives for MeitY-approved projects, aiming to position the state as a global electronics manufacturing hub.
The Gujarat government has introduced the Gujarat Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme-2025 (GECMS-2025), which aims to position the state as a global powerhouse for electronic component production.
The programme, announced by Chief Minister Shri Bhupendra Patel, aligns with the Centre’s Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS). It intends to attract over ₹35,000 crore in new investments and generate high-skilled employment.
Projects authorised by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and built in Gujarat will receive 100% government aid, as well as extra state-level incentives, under GECMS 2025. Incentives will be given within 30 working days of the central money being released, ensuring that industries receive timely support. The policy also provides turnover-linked benefits for six years.
Key focus areas include the production of multi-layer and HDI printed circuit boards, lithium-ion cells, SMD passive components, display and camera modules, electromechanical parts, and related specialised gear. Gujarat colleges can receive funds of up to ₹12.5 crore to establish Centres of Excellence, Applied Research Labs, and Finishing Schools, promoting research and development.
Eligibility and Application:
The Gujarat State Electronics Mission (GSEM) will manage the policy’s implementation, which will continue within the central ECMS scheme timeframe. Furthermore, need-based assistance will be provided to create shared infrastructure in electronics clusters.
Gujarat’s goal with this project is to strengthen its position in global electronics supply chains, minimise import dependency, and foster innovation-led growth in the electronics ecosystem.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
The government has opened applications for a new scheme offering reduced import duties on electric cars in exchange for local manufacturing and investment commitments.
The Indian government has opened an online portal to invite applications for its new electric car manufacturing project, the Scheme to Promote Manufacturing of Electric Passenger Cars in India (SPMPCI). Open until October 21, 2025, the plan allows global automakers to import electric cars (EVs) at much lower customs taxes in exchange for considerable investment and manufacturing commitments in India.
Under the initiative, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) can import Completely Built-Up (CBU) electric automobiles with a minimum Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF) value of $35,000 at a 15% customs charge for five years—a reduction from the typical duty rate of 70-110%.
Manufacturers must invest at least ₹4,150 crore in local production to receive the benefits, which are limited to 8,000 imported units per year.
To qualify for tariff discounts, participating enterprises must develop manufacturing facilities in India and begin commercial production within three years of approval. Furthermore, they must produce 25% domestic value addition (DVA) within the first three years, rising to 50% by the fifth year.
A key requirement of the policy is that companies must provide a bank guarantee, which is a promise from a bank in India to cover the customs duty that is not collected. This guarantee will be used if the company does not fulfil its investment or DVA commitments.
The finalised guidelines incorporate significant changes from prior versions. Most notably, the scheme now allows brownfield investments as long as they are physically separate from current facilities. It also broadens the investment scope to encompass research and development (R&D) and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. While R&D spending is not limited to the entire committed investment, charging infrastructure can only get up to 5% of the investment.
With this scheme, the government hopes to entice major EV manufacturers to establish operations in India, support local manufacturing, and advance the country’s transition to sustainable mobility.
Further details and official notifications related to the scheme are available at https://heavyindustries.gov.in/scheme-promote-manufacturing-electric-passenger-cars-india-0.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
HPCL is investing ₹2,000 crore to build 24 biogas plants, supporting India’s shift to clean, domestic energy.
HPCL Renewable and Green Energy Ltd aims to invest ₹2,000 crore over two to three years to establish 24 compressed biogas (CBG) plants in India.
The program is an important step towards HPCL’s commitment to sustainability and better energy solutions. Two CBG plants have already been commissioned, and the business plans to commission another 24. Each facility will be able to manufacture 10 to 15 tonnes of CBG per day using feedstock such as agricultural waste, cow manure, and sewage water.
Mohit Dhawan, CEO of HPCL Renewable and Green Energy Ltd, stated, “We are boosting efforts to provide cleaner fuel alternatives by deploying biogas systems. The new CBG facilities will dramatically reduce emissions while supporting circular economy techniques.
The decision helps India’s climate action agenda, which aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070. CBG has emerged as an important alternative fuel in this endeavour, particularly in the transportation and domestic energy sectors.
The Indian government has mandated the CBG account for at least 1% of the gas used in automobiles and for household cooking beginning in April 2025. This objective is expected to rise to 5% by 2028–29.
Vikas Singh, Director, Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, stated, “The government aims to increase the usage of cleaner gases such as CBG. By 2028-29, we estimate 480 CBG facilities, including 195 developed by public sector oil and gas corporations.”
At present, India uses about 28 million standard cubic meters per day (MMSCMD) of gas for transportation and cooking. This demand is predicted to reach 44 MMSCMD by 2028-29. Given that India currently imports roughly half of its gas in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG), expanding CBG production domestically will help reduce reliance on imports and improve energy security.
HPCL remains focused on driving sustainable energy solutions and supporting India’s transition to cleaner fuels.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Hyundai Motor India has tested over 4.25 million engines using zero-emission, fuel-free Cold Bed Engine Testing, advancing its net-zero and green manufacturing goals.
Hyundai Motor India Limited (HMIL), India’s premium provider of smart mobility solutions, has reached a significant milestone in sustainable manufacturing by successfully testing over 4.25 million engines with its revolutionary Cold Bed Engine Testing technology. This approach removes the need for fuel, coolant, and water, allowing for a completely clean and zero-emission testing method.
Revolutionising Engine Testing
Cold Bed Engine Testing, which was introduced in 2013, allows HMIL to evaluate engine performance using electricity generated from renewable energy rather than traditional fuel-based methods. The technology employs high-precision sensors to monitor important engine parameters such as crankshaft angle, chamber pressure, and compression, guaranteeing that each engine fulfils strict quality criteria while emitting no emissions.

Gopalakrishnan CS, Director and Chief Manufacturing Officer, HMIL, stated, “At Hyundai Motor India, innovation and sustainability go hand in hand. By testing over 4.25 million engines using zero-emission Cold Bed Engine Testing, we’ve curbed 2 million kg of CO₂ and saved US $1 million, while ensuring world-class quality through our fully automated, fuel-free process. As we mark 30 years of ‘Make in India, Made for the World’, we stay committed to driving a greener, smarter future.”
Environmental and Economic Impacts
Through clean testing, HMIL has reduced CO₂ emissions by almost 2 million kg, contributing to cleaner air and more sustainable mobility. Furthermore, the use of this system has saved the corporation roughly $1 million in operational expenditures by eliminating the requirement for gasoline, coolant, and water during engine testing.
How Technology Works
Cold Bed Engine Testing uses an electric motor to rotate each engine’s crankshaft. Sensors measure engine compression, chamber pressure, crankshaft angle, and other performance characteristics to assess engine worthiness. The completely automated system, which is integrated with Industry 4.0 technology, digitally archives all test data, allowing for future research and development and continual improvement.
Driving a Greener Automotive Future
This fully automated, zero-emission process demonstrates HMIL’s dedication to innovation, quality, and environmental responsibility. Cold Bed Engine Testing, which is part of Hyundai’s global aim to reach net-zero emissions by 2045, demonstrates how sustainable practices are being integrated into production operations to create a smarter, greener future.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Schneider Electric and Nvidia have partnered to develop sustainable, AI-ready infrastructure, supporting Europe’s push to build next-gen AI factories.
Schneider Electric, a global leader in digital energy management and automation, today announced a strategic alliance with NVIDIA to address the growing demand for sustainable, AI-ready infrastructure. The news was made during the NVIDIA GTC Paris.
The collaboration is centred on cooperative R&D activities in power, cooling, controls, and high-density rack systems to enable the next generation of AI factories in Europe and elsewhere. It supports the European Union’s “InvestAI” project, which aims to raise €200 billion in AI investments, as well as the “AI Continent Action Plan”, which aims to establish 13 AI factories and up to five AI gigafactories across Europe.
Olivier Blum, CEO of Schneider Electric, stated, “Schneider Electric and NVIDIA are not just partners — our teams are driving advanced R&D, co-developing the infrastructure needed to power the next wave of AI factories globally. Together, we’ve seen tremendous success in deploying next-generation power and liquid cooling solutions for AI data centres.”
Jensen Huang, creator and CEO of NVIDIA, commented, “AI is the defining technology of our time—the most transformative force reshaping our world. Together with Schneider Electric, we are building AI factories: the essential infrastructure that brings AI to every company, industry, and society.”
Schneider Electric introduced new AI-ready data centre solutions, including the EcoStruxure™ Pod and Rack Infrastructure and an Open Compute Project-inspired rack system that supports the NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 platform. These solutions are based on NVIDIA’s MGX modular architecture, demonstrating Schneider’s integration into the NVIDIA HGX and MGX ecosystems.
In addition, Schneider and NVIDIA collaborated on reference designs for electrical and liquid cooling systems, and Schneider is now a certified CDU provider for NVIDIA. These designs also incorporate Motivair solutions, which Schneider Electric bought in March 2025.
The reinforced alliance intends to speed the implementation of scalable, AI-optimised infrastructure, thereby boosting global advances in artificial intelligence.
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.