Latest welding trends are impacting the aerospace
By OEM Update Editorial September 1, 2023 11:47 am IST
Recent trends in welding technology are reshaping the aerospace industry, enhancing efficiency, quality, and safety. According to Dr. T.J. Prasadrao, Executive Director (Technical), D & H Sécheron, automation, advanced techniques, and materials innovation drive change, while collaborative robots revolutionise welding processes.
How are the latest welding processes trends in welding technology impacting the aerospace industry?
Several significant trends are influencing the aerospace industry in welding technology. One of the key impacts is heightened efficiency as emerging technologies within aviation welding expedite production processes, resulting in increased efficiency in production. Moreover, implementing advanced welding techniques promises to enhance the quality of welds. This improved weld quality is particularly crucial given the importance of safety in the aerospace sector.
An additional impact centre around is cost reduction. As these novel welding technologies become more prevalent, the potential for reducing manufacturing costs emerges, contributing to economic benefits for the aerospace industry. An equally substantial influence arises from innovation in materials. The progression of welding technologies often coincides with the development of novel materials, which in turn wields a substantial influence on the aerospace domain.
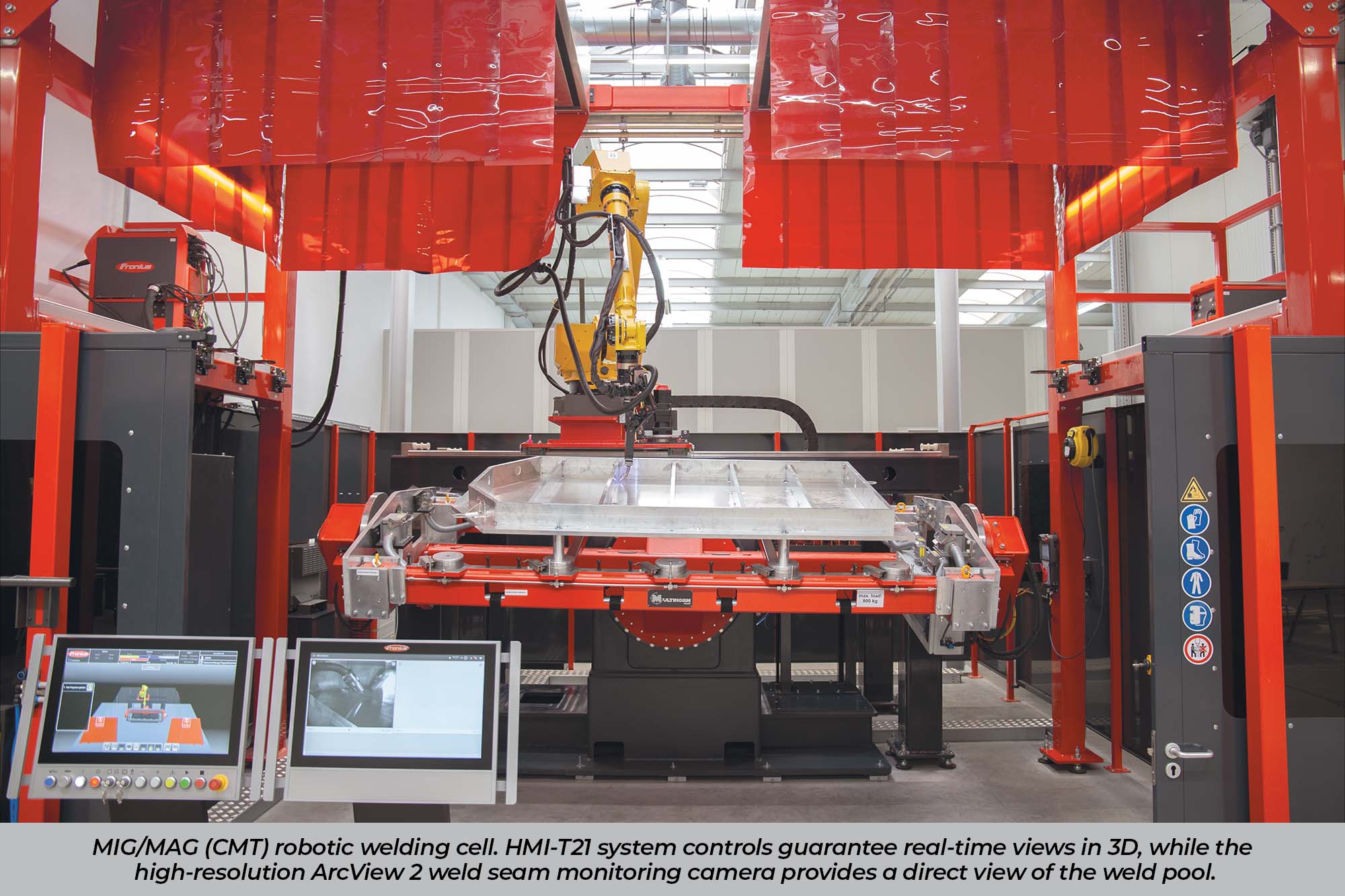
Furthermore, the trend towards automation within the welding industry carries noteworthy implications. By incorporating automation, the aerospace industry stands to gain more consistent and dependable results from welding processes. Given aerospace’s precision and reliability demands, this trend holds particular significance within this sector.
Could automated processes and robotic welding replace manual welding for refinishing components?
Yes, automated processes and robotic welding have the potential to replace manual welding for refinishing components, driven by several compelling reasons. One notable advantage is the consistency and precision offered by robots. They execute tasks with unwavering uniformity and high accuracy, resulting in superior-quality welds and virtually zero defects.
Efficiency is another compelling factor. Automated processes operate continuously without breaks, leading to higher productivity. Additionally, robots often outpace human workers in speed, further enhancing overall efficiency.
Safety considerations also favour the utilisation of robots. Welding involves inherent risks due to the generation of heat and intense light. Integrating robots in this context can significantly reduce potential hazards to human workers, promoting a safer working environment.
The upfront investment in robotic welding technology might be substantial from a financial perspective. Nonetheless, the increased efficiency and decreased labour costs can lead to significant savings over time.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that while robotic welding boasts numerous advantages, its suitability for all tasks may be limited. Complex or custom jobs still necessitate the skill and expertise of human welders. Thus, a hybrid approach that combines manual and robotic welding might present the most optimal solution across various cases and scenarios.
How is augmented reality being utilised to train and enhance the skills of welders?
Augmented Reality (AR) is on the rise within the welding domain, particularly for the training and advancement of welders, manifesting in various ways.
Firstly, AR enables welders to engage in virtual practice, honing their skills in a simulated environment before moving on to real-world tasks. This dual benefit conserves material costs while furnishing a secure, risk-free avenue for practice. Secondly, AR systems provide real-time feedback to welders, pointing out errors and suggesting avenues for improvement. This dynamic feedback loop expedites the learning curve and facilitates swift skill development.
Moreover, AR can simulate intricate or dangerous scenarios that might be challenging to replicate. This facet empowers welders to cultivate familiarity and confidence in managing challenging situations. Furthermore, AR can offer step-by-step visual guidance throughout welding, overlaying pertinent information onto the actual view. This proves especially advantageous for intricate or infrequently executed tasks.
AR’s capacity to enable remote learning and collaboration emerges as another asset. By harnessing AR technology, welders can partake in learning and collaborative endeavours from disparate locations, a particularly pertinent capability amid the ongoing pandemic and within organisations spanning multiple geographical areas. And it can help standardise training methodologies. AR aids in unifying training procedures, ensuring consistent and high-quality instruction for welders, irrespective of their geographical location.
The strategic integration of AR into training initiatives equips companies to enhance the proficiency of their welders in a more streamlined manner. Consequently, this integration promises to augment quality and productivity within welding practices.
What are the potential applications for cobots in welding processes within the aerospace industry?
Collaborative robots, often referred to as Cobots, are increasing in adoption across diverse industries, including aerospace, owing to their capacity to work harmoniously alongside humans with safety and efficiency in mind. Within the realm of welding processes specific to the aerospace sector, Cobots present a range of potential applications:
Precision welding: Given the demand for high-precision welding in aerospace components, Cobots stand poised to execute such tasks with remarkable consistency and accuracy, offering a solution for achieving meticulous results.
Repetitive tasks: Cobots tirelessly perform repetitive tasks, rendering them well-suited for the prolonged production runs often encountered in aerospace manufacturing.
Challenging locations: Cobots can be outfitted with specialised tools and programmed to navigate intricate spaces that might pose challenges for human welders, extending their reach to such demanding areas.
Training: Cobots can play a role in training scenarios, allowing new welders to gain hands-on experience while sidestepping potential risks of injury.
Flexible production: Cobots’ ease of reprogramming and adaptability renders them conducive for custom, low-volume production runs. This adaptability aligns well with the aerospace sector’s propensity for frequent changes in component specifications.
While Cobots hold promise for substantial benefits, their effective integration necessitates meticulous planning and thoughtful consideration. Aspects such as safety protocols, the necessity for human supervision, and the seamless assimilation of Cobots into existing workflows warrant deliberate attention. Nonetheless, a well-orchestrated approach positions Cobots as a valuable asset in the ongoing aerospace industry endeavour to augment efficiency, quality, and safety.
What factors have contributed to the recent advancements in automation for welding processes?
Following are some factors that have contributed to the recent advancements in automation for welding processes.
Improved technologies and equipment: Integrating cutting-edge equipment and technologies has been pivotal in automating welding processes. This encompasses the deployment of welding robots, sophisticated automated welding systems, and state-of-the-art welding tools.
Enhanced precision and accuracy: Automation has engendered a notable enhancement in the precision and accuracy of welding procedures. This, in turn, has yielded tangible improvements in weld quality, effectively curbing the occurrence of defects.
Improved productivity: Automation has emerged as a potent catalyst for elevated productivity and heightened efficiency in welding operations. This transformative effect translates into swifter welding durations and augmented production rates.
Augmented safety: Automation has ushered in improved safety protocols within welding processes. Automation has fostered a safer work environment by reducing workers’ exposure to hazards, effectively curtailing accidents.
Cost optimisation: Automation has engendered cost-cutting benefits within welding processes through several avenues. These encompass the reduction in manual labour requirements, the minimisation of errors, and the optimisation of production efficiency. Collectively, these contribute to multifaceted cost reductions.
In summation, the amalgamation of these diverse factors has catalysed the recent strides witnessed in automation for welding procedures and has also spurred advancements that permeate various welding dimensions.
What strategies can raise awareness among skilled workers to adopt automation in welding?
Raising awareness among skilled workers regarding the integration of automation in welding can be accomplished through a range of strategic approaches:
First, prioritise education and training by orchestrating workshops, seminars, and training sessions. These initiatives can elucidate the advantages of automation in welding, incorporating live demonstrations of automated welding procedures, hands-on experience with automated equipment, and presentations elucidating the impact of automation on productivity and safety.
Maintain a steady dialogue with workers regularly regarding the company’s automation plans. Employ channels such as newsletters, emails, meetings, and bulletin board postings to convey the organisation’s direction transparently. By fostering transparency, concerns and resistance can be mitigated.
Incorporate workers into the automation process as an involvement strategy. Seek their input on automation plans, engage them in testing and implementing automated processes, and encourage them to express their thoughts and reservations. This participatory approach fosters a sense of investment in the process, thereby diminishing perceived threats.
Assuage worker apprehensions through reassurance. Clarify that automation is intended not to supplant them but to augment their roles. Emphasise the continued value and indispensability of their skills, knowledge, and expertise, underscoring that while certain tasks may be automated, their contributions remain pivotal.
Promote upskilling as a proactive measure. Create avenues for workers to acquire new proficiencies related to automation. This encompasses training in operating and maintaining automated equipment and venturing into domains such as programming and data analysis. By positioning automation as an avenue for career advancement, the narrative shifts from job jeopardy to professional growth.
Highlight success stories as a persuasive tactic. Share instances of other enterprises or industries that have seamlessly adopted welding automation, delineating the tangible benefits they’ve reaped. These tangible examples crystallise the potential advantages of automation for workers, making the concept more real.
By deploying these strategies, organisations can effectively cultivate awareness and understanding among skilled workers regarding the integration of automation in welding.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.