Changing fuel with the rise of biotransformed ethanol and renewable chemicals
By OEM Update Editorial July 16, 2024 7:03 pm IST
The ethanol industry sector, once dominated by traditional petroleum-based processes, is now undergoing a remarkable transformation. In this article, we will delve into the evolving world of fuel ethanol, while emphasising the role of biotransformation, biomanufacturing, and the promise of renewable chemicals.
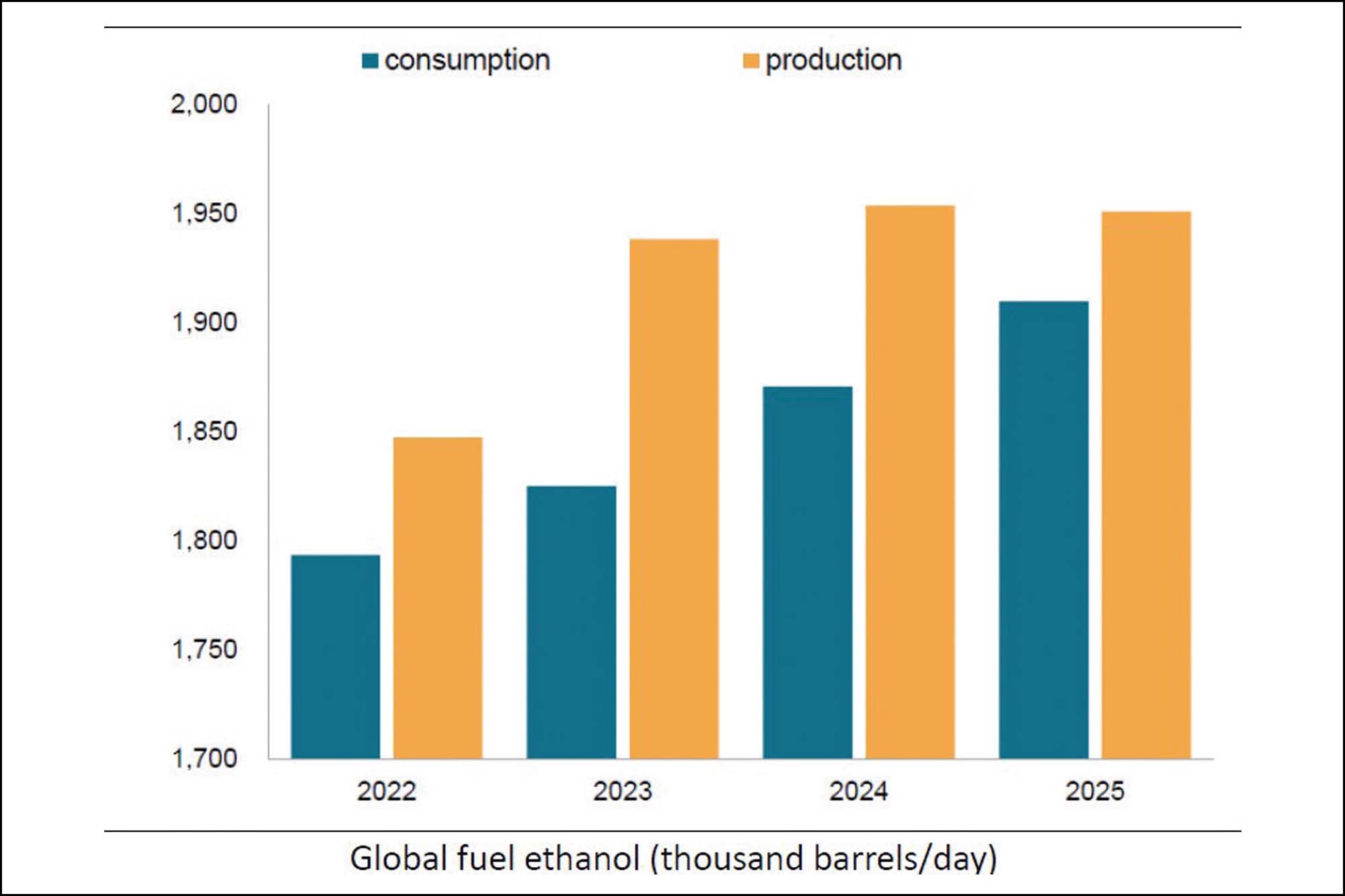
One of the most well-established applications of bioethanol is its use as a fuel additive in gasoline. Blending bioethanol with gasoline reduces greenhouse gas emissions and enhances octane ratings, leading to cleaner combustion and improved engine performance. Figure 1 illustrates the global consumption/ production of bioethanol as a fuel, showcasing its steady growth over the years.
However, advancements in bioethanol technology have expanded its role beyond conventional fuel applications. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), for instance, is garnering significant attention as a means to decarbonise the aviation sector. Bio
ethanol-derived SAF offers a promising solution due to its compatibility with existing aircraft engines and infrastructure.
Bioethanol as a feedstock
Bioethanol serves as a precursor for various renewable materials, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products. One notable example is bioplastics, which can be synthesised from bioethanol through fermentation or chemical processes. These bioplastics exhibit similar properties to conventional plastics but with the added benefit of being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, thus mitigating plastic pollution and resource depletion. Figure 1 illustrates the global production capacities of bioplastics between 2022-2027.
Additionally, bioethanol-derived chemicals find applications in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to cosmetics. For instance, ethanolamines are vital components in various personal care products and detergents. By replacing petroleum-derived chemicals with bioethanol equivalents, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on finite fossil resources.
Biomanufacturing facility
A biomanufacturing facility is a specialised facility where biological products are manufactured on a large scale. These facilities are designed to produce a wide range of products, including biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, enzymes, and bio-based materials. Biomanufacturing processes typically involve living organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or mammalian cells, to produce the desired products through fermentation, cell culture, or other bioprocess techniques.
Biomanufacturing facilities require highly controlled environments to ensure the safety, purity, and efficacy of the products being produced. They have state-of-the-art equipment and technology for fermentation, purification, and other manufacturing processes.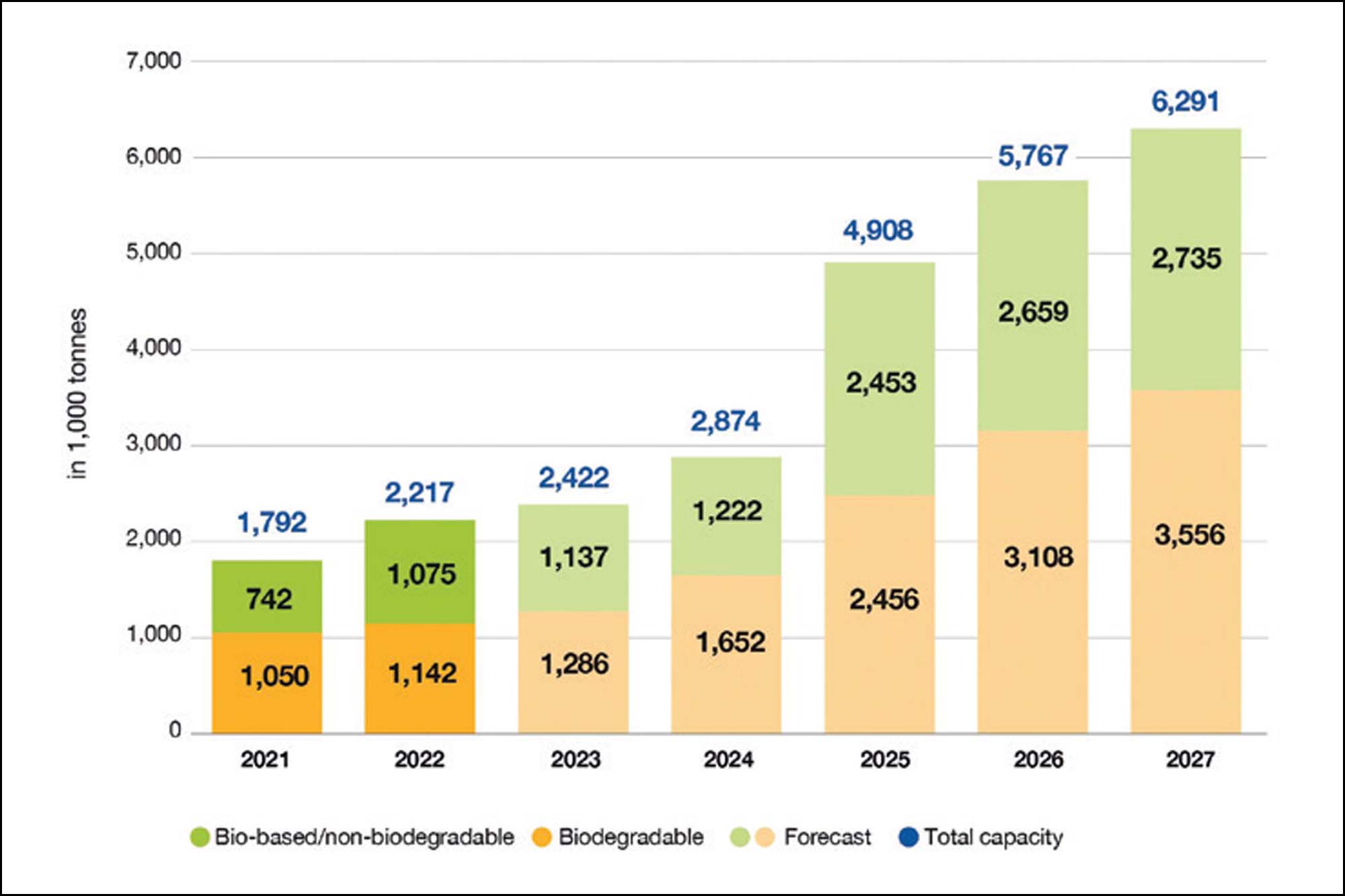
Most organic compounds and polymers are still produced from petroleum and other fossil fuels. Biomass-based renewable chemicals and materials will be essential in the shift from the fossil-based economy to the bio-based circular economy. The formation of Biomanufacturing hubs will help mitigate climate change.
Need for the biomanufacturing facility
- Strategy for ensuring long-term economic and environmental sustainability
- Does not contribute to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in contrast to fossil fuels
- To reduce the emission of greenhouse gases
- An over-dependency on fossil fuel imports
- Reducing chemical waste and the emission of hazardous by-products
- Diversify feedstock sources that support the nation’s industrial base
- “Safe by Design” processes and products
- Recycling-friendly chemicals and materials save money, resources, and energy
- Deployment in rural areas will stimulate regional and rural development
Biorefinery
Biorefinery integrates various biomass conversion processes to produce a wide range of valuable products, akin to the conventional petroleum refinery but using renewable biomass as the feedstock. Biorefineries utilise biomass resources by extracting multiple products, including biofuels, biochemicals, biopolymers, and other biobased materials while minimising waste and environmental impact.
Conclusion
The ethanol industry has shifted towards sustainable practices and renewable resources. Bioethanol, once primarily used as a fuel additive, now is used in transportation and renewable materials production. This evolution underlines the importance of biotransformation and biomanufacturing in shaping a greener future. India’s BioE3 Policy exemplifies a strategic approach to biomanufacturing, aiming to drive green growth and socio-economic development through innovation and collaboration. The Interim Budget 2024-25 proposes a new scheme of bio-manufacturing and bio-foundry which will provide environmentally friendly alternatives such as biodegradable polymers, bioplastics, biopharmaceuticals, and bio-agri-inputs. By fostering high-performance biomanufacturing and integrating biotechnology with various sectors, India aims to accelerate its transition towards a sustainable bioeconomy, while prioritising biosafety, ethics, and equitable access.
In conclusion, the ethanol industry’s transformation towards sustainability underscores the critical role of biotransformation, biomanufacturing, and renewable chemicals. This will drive global efforts to transition towards a bio-based circular economy facilitating a cleaner greener future.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.