Materials and technology are enhancing the die and mould industry
By OEM Update Editorial December 29, 2023 7:16 pm IST
The die and mould industry thrives on material selection and technological innovations to drive precision and efficiency. Akshay Kalyanpur, Director, Sridevi Tool Engineers Pvt. Ltd. discusses that factors influencing material choice are diverse, impacting manufacturing processes significantly. Additionally, technological advancements, including AI and additive manufacturing, shape the industry’s future.
Please discuss the primary considerations for selecting materials used in mould manufacturing.
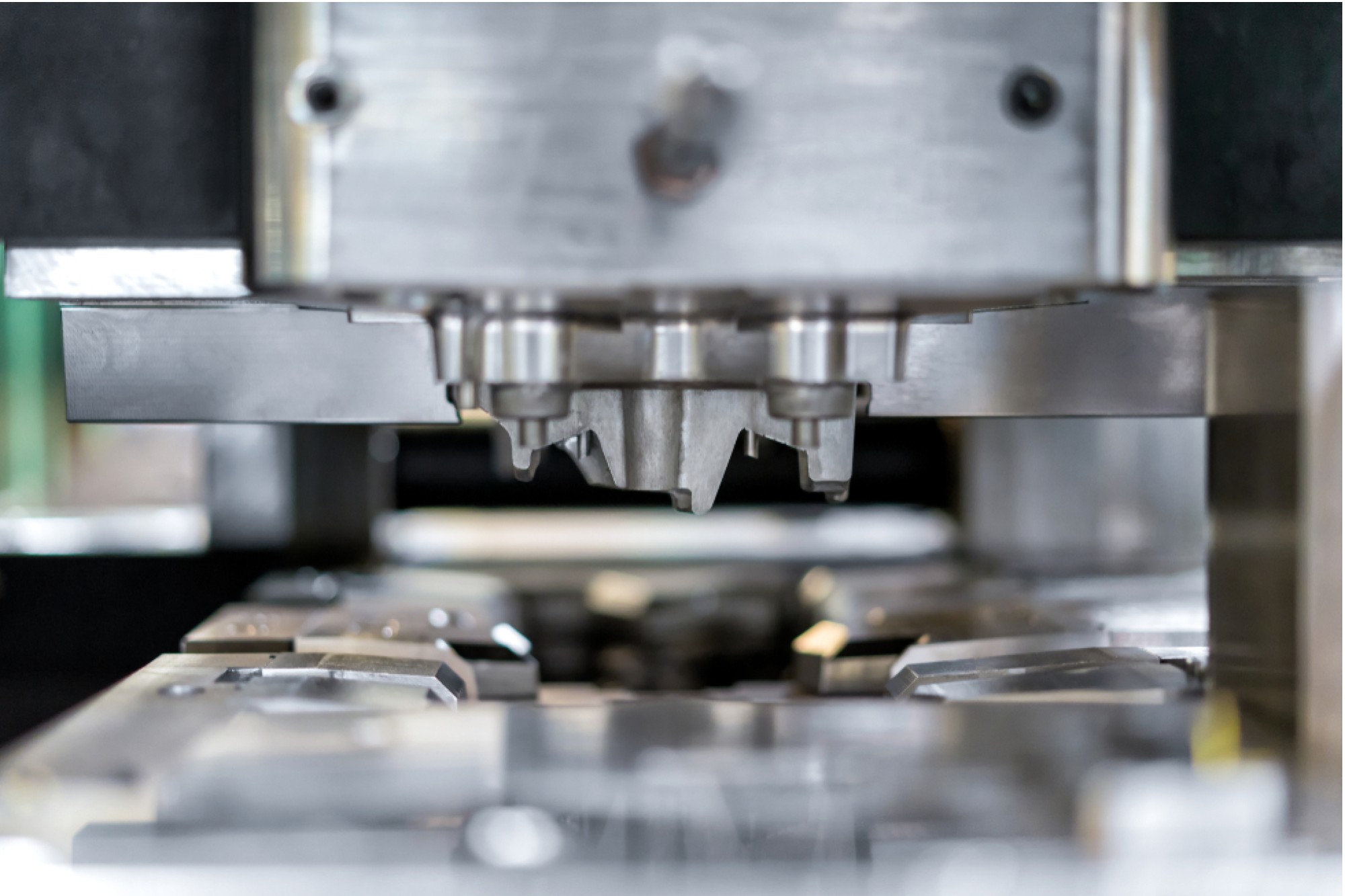
The choice of materials for moulds heavily depends on several key factors. Firstly, considering the expected lifespan of the mould is crucial. Pre-hardened steels are suitable for shorter lifespans of up to 0.5 million shots. However, hardened mould steels are preferred for longer lifespans of up to a million shots, particularly for smaller part sizes.
Secondly, the required surface finish of the visible part plays a significant role. Achieving high gloss and clear parts necessitates using ESR grade or clean, high chrome steels. These materials can be hardened or selected from specific clean steels available in pre-hardened varieties.
Another vital factor is the nature of the polymer being moulded. If the plastic is abrasive, corrosive, or contains glass fibres, it is advisable to use hardened mould steels to withstand these conditions effectively.
Lastly, areas within the mould that demand high heat dissipation call for specific materials like Ti-Cu, or other high-conductive steels. These materials facilitate faster heat extraction, especially in areas that are difficult to cool adequately.
The mould manufacturing process can be divided into two parts: tasks performed before hardening and those carried out after hardening. Milling hardened steel requires specialised machinery with high speed spindle, rigid frame, and special tooling and programming techniques. Adjusting cutting parameters becomes essential to prolong the lifespan of cutting tools and machine components.
What latest technologies are being employed in the die and mould industry to enhance precision, efficiency, and quality in production?
The core technologies used in the die and mould industry are design software, programming software, simulation software, CNC machining and Injection moulding. These technologies continue to progress steadily, contributing to comprehensive improvements in quality, efficiency, and various other aspects of development.
The integration of AI in the Die and Mould industry holds immense potential for transformation, and it could be a game changer. This industry thrives on knowledge, as each mould presents distinct challenges and requires unique solutions. AI can analyse these patterns by capturing data during mould manufacturing and problem-solving processes and offer tailored solutions for upcoming moulds. This shift would move troubleshooting from relying on instincts to a systematic approach driven by AI-generated insights. From design to production, AI offers boundless possibilities and could revolutionise various stages of the manufacturing process.
What are the various manufacturing trends used by Mould makers to meet the needs of the OEMs in the industry?
Automotive die mould manufacturers frequently adopt modern technologies based on customer demands. For instance, integrating 3D-printed conformal cooled inserts becomes necessary if clients seek faster cycle times. Some customers request GPS-enabled chips for asset tracking, while others ask for wireless digital shot counters to monitor production volumes. Alongside technological advancements, one more important trend that I must highlight is localisation. Each year, the number of tools localised for most OEMs continues to rise.
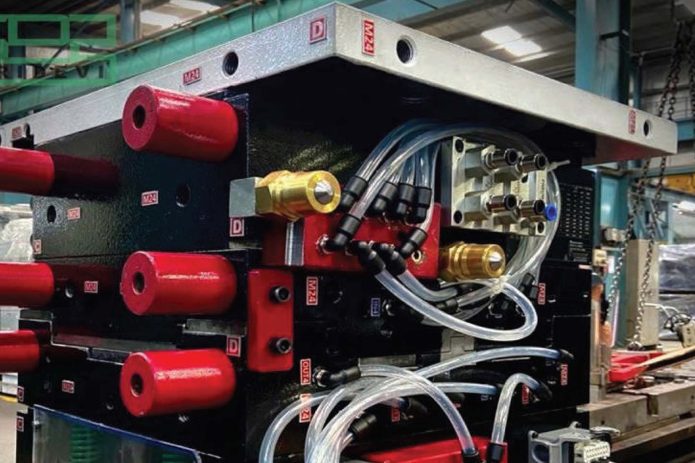

How do the growth opportunities in injection moulding influence the die and mould industry?
There is a direct correlation between Injection moulding businesses and the die-mould industry. When the quantity of plastic parts escalates beyond the capacity of a single mould, customers often ask for duplicate moulds to meet the rising demand. Another approach involves considering multi-cavity moulds that can operate on larger moulding machines. Some customers prioritise reducing cycle times to enhance overall throughput. Additionally, the trend of lightening car components for increased efficiency leads to replacing certain metal parts with plastic. All of these factors significantly impact the die and mould industry.
How are technologies like 3D printing leveraging component and equipment part manufacturing in India?
3D printing has had the most impact on prototyping and small production businesses. 3D printing enables rapid and cost-effective production of prototypes. Conventional prototyping methods often involve time-consuming processes like CNC machining, which can take days or weeks. Through 3D printing, companies can provide intricate and customised designs, catering to on-demand or small-batch production with exceptional flexibility.
Please discuss standards governing the production, usage, and disposal of dies and moulds and their impact on manufacturers.
ISO 14001 is the global benchmark for environmental management systems (EMS). Although Indian die and mould manufacturers don’t need certification presently, there’s a growing trend internationally, led by OEMs and Injection Moulders, to collaborate with EMS-certified die and mould makers. This trend is expected to soon emerge in India as well.
EMS offers a structured approach for organisations to develop, implement, and consistently enhance their environmental performance. Its key advantage is prompting efficiency improvements across the manufacturing process. By minimising waste and unlocking hidden capacity, the expenses in implementing and sustaining EMS are offset.
Steel constitutes a significant part of moulds, and when discarded, it typically returns to mills for recycling into new steel. Other parts are disposed of following manufacturers’ guidelines, while there’s a rising awareness to reduce materials like Beryllium copper as part of efforts to minimise environmental impact.
How is additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing, being integrated into the die and mould industry, and what are the benefits of this technology in this specific sector?
Various metals, ranging from stainless steel to copper, offer extensive options for 3D printing purposes. The most popular application of 3D-printed metal inserts in moulds is to enhance cooling efficiency in areas where traditional cooling methods are impractical. Customers have experienced significant cycle time reductions, up to 30%, by incorporating 3D-printed inserts with conformal cooling. This approach yields advantages such as increased hourly throughput, cost reduction, eliminating the necessity for duplicate moulds, avoiding the need to operate two injection moulding machines for increased volume, improved part appearance, and enhanced PIST (Percent of Inspection Points that Satisfy the Tolerances indicated on the design.)
How does the evolution of 3D printing impact small-part production and its potential influence on traditional tooling methods like soft tools?
As 3D printing advances, it is reshaping the landscape for small-part production, potentially phasing out soft tools. With current technologies, 3D printing achieves injection mould-level quality and strength, enabling medium to small-volume production of these parts. While additive manufacturing might not entirely replace high-volume, high-quality production moulds and dies, it serves as a valuable complement to them.
The automotive and motorcycle industries are experiencing shortened development cycles, impacting the lead times for die and mould manufacturers. The focus remains on discovering methods to expedite tool production continually. Additionally, digitisation is pervasive, and embedded electronics are becoming increasingly prevalent—indicating a substantial future role for AI in these advancements.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.