AL and ML in healthcare
By OEM Update Editorial June 18, 2024 6:37 pm IST
This article provides an overview of the high-level impact of AI/ML on the healthcare industry, potential use cases, and ethical dilemmas in the form of some KEY questions that get a directional response to set the thought process rolling further.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) drive transformations across numerous industries. AI in healthcare shows up in several ways, such as finding new links between genetic codes, powering surgery-assisting robots, automating administrative tasks, and personalising treatment options.
The impact of AL/ML is profound in data and research-intensive sectors like pharmaceuticals. AI is revolutionising processes ranging from enhancing candidate selection for clinical trials to expediting the development of new drugs. In this dynamic industry, embracing AI has become imperative for organisations aiming to maintain competitiveness amidst rapid advancements.
The modern healthcare industry possesses one of the largest collections of data sources, fitting seamlessly into the Big Data paradigm of today’s digital world. These sources include patient digital health records, clinical trial details, hospital management data, and vital health data gathered by using modern wearable devices. These sources continuously generate data that require segmentation, contextualisation, data mining, and the creation of insights as part of the first-level analytics.
This, combined with modern ML algorithms to develop forecasting and predictive models, enables predictive decision-making and is the primary focus going forward.
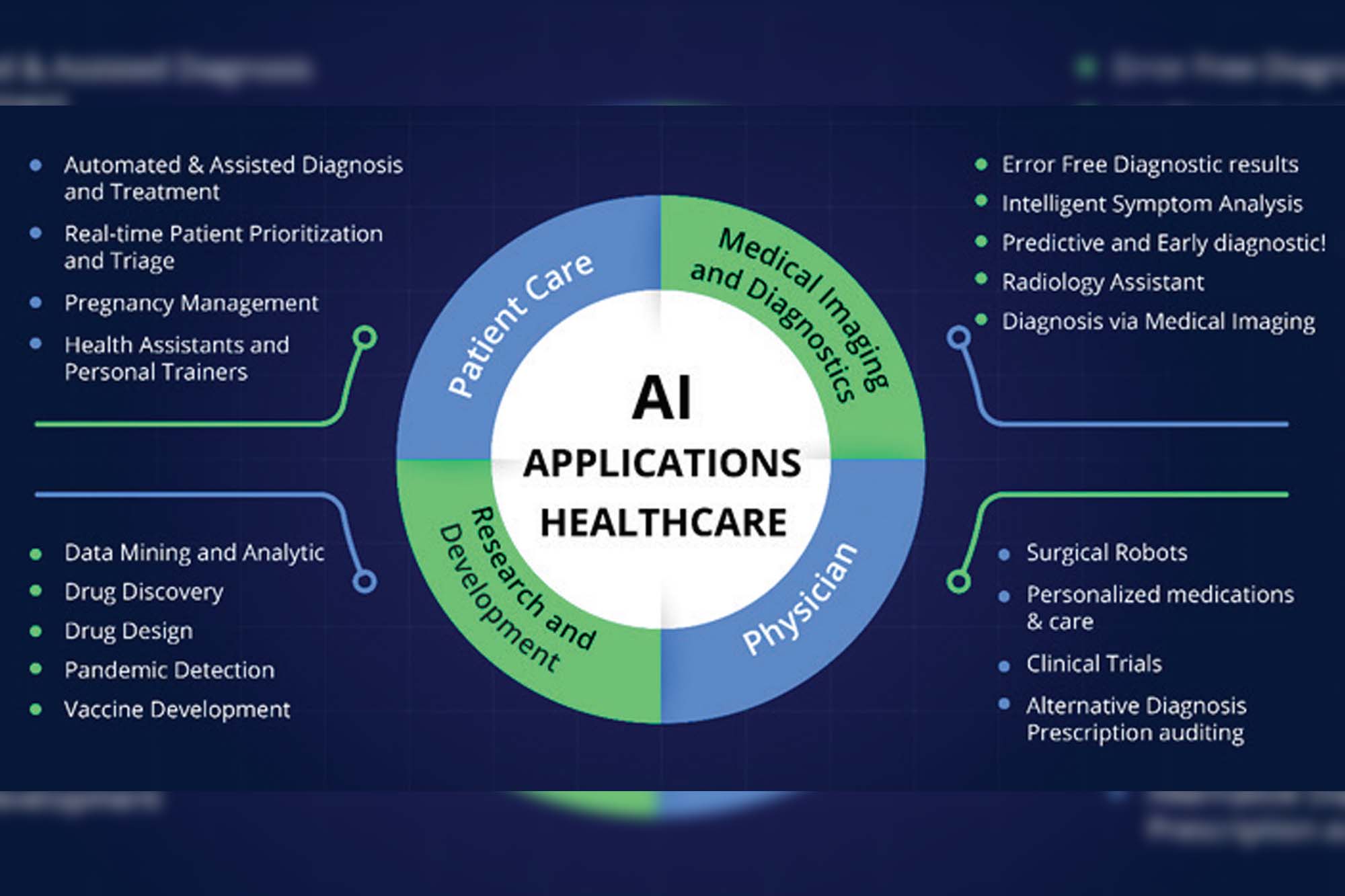
AI has a huge impact on healthcare in various arenas, such as improving medical diagnosis, Speeding up drug discovery, Transforming patient experience, Managing healthcare data, Performing robotic surgery, and so on. AI and ML technologies can sift through enormous volumes of health data—from health records and clinical studies to genetic information—and analyse it much faster than humans.
Here are some questions with directional responses based on our limited understanding of this domain. In the prevalent context, they should be answered. The responses are not “comprehensive”. However, the aim is to provide direction and set the discussion rolling by capturing some unique trends and establishing a baseline understanding of these key questions.
How do you see AI revolutionising drug discovery in the pharmaceutical industry? Can AI help in discovering new drug molecules that could help treat deadly and chronic diseases like cancers and AIDS?
AI is about combining the “huge immense historical data” to build models that could replicate decision-making and business logic to arrive at the desired outcomes by leveraging computing power. In Pharma – new molecules are a process of exploration and experimentation that could be accelerated by leveraging this approach. A huge amount of research is happening for finding solutions for diseases like Cancers / AIDS / HIV prevention – ML approaches have been used to identify potential candidates for HIV in healthcare settings in the U.S. and Denmark and in a population-based research setting in Eastern Africa. Although still in the proof-of-concept stage, other applications include ML with smartphone-collected and social media data to promote real-time HIV risk reduction, virtual reality tools to facilitate HIV serodisclosure, and chatbots for HIV education. ML has also been used for causal inference in HIV prevention studies.
What are the challenges in implementing AI-driven solutions in healthcare, particularly in the context of regulatory compliance?
The foundation of AI and ML approaches relies on context-based historical data. In healthcare, key challenges include data ownership, confidentiality, and ensuring the availability of data while maintaining anonymity. The Patient’s Healthcare Records (PHR) are the key components for any healthcare-related progress. The ownership of this data has its policies and outlines for various countries to legalise this data usage for some commercial-centric research across the world.
Please suggest a specific example of AI used to discover or develop a new drug.
Insilico Medicine, a biotech company headquartered in Hong Kong, has created the world’s first AI-designed anti-fibrotic small molecule inhibitor drug for testing in human patients. (First Posted: July 11, 2023 https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05938920)
How do you envision the role of AI evolving in personalised medicine and patient care?
AI leverages sophisticated computation and inference to generate insights, enables the system to reason and learn, and empowers clinician decision-making through augmented intelligence. The whole protocol for the clinician, from building context about the patient to being able to make a decision tree to arrive at the root cause and hence treatment for the specific patient’s symptom, would be extremely fast, and as the AI/ML models go through the learning process, they will become more and more reliable and accurate.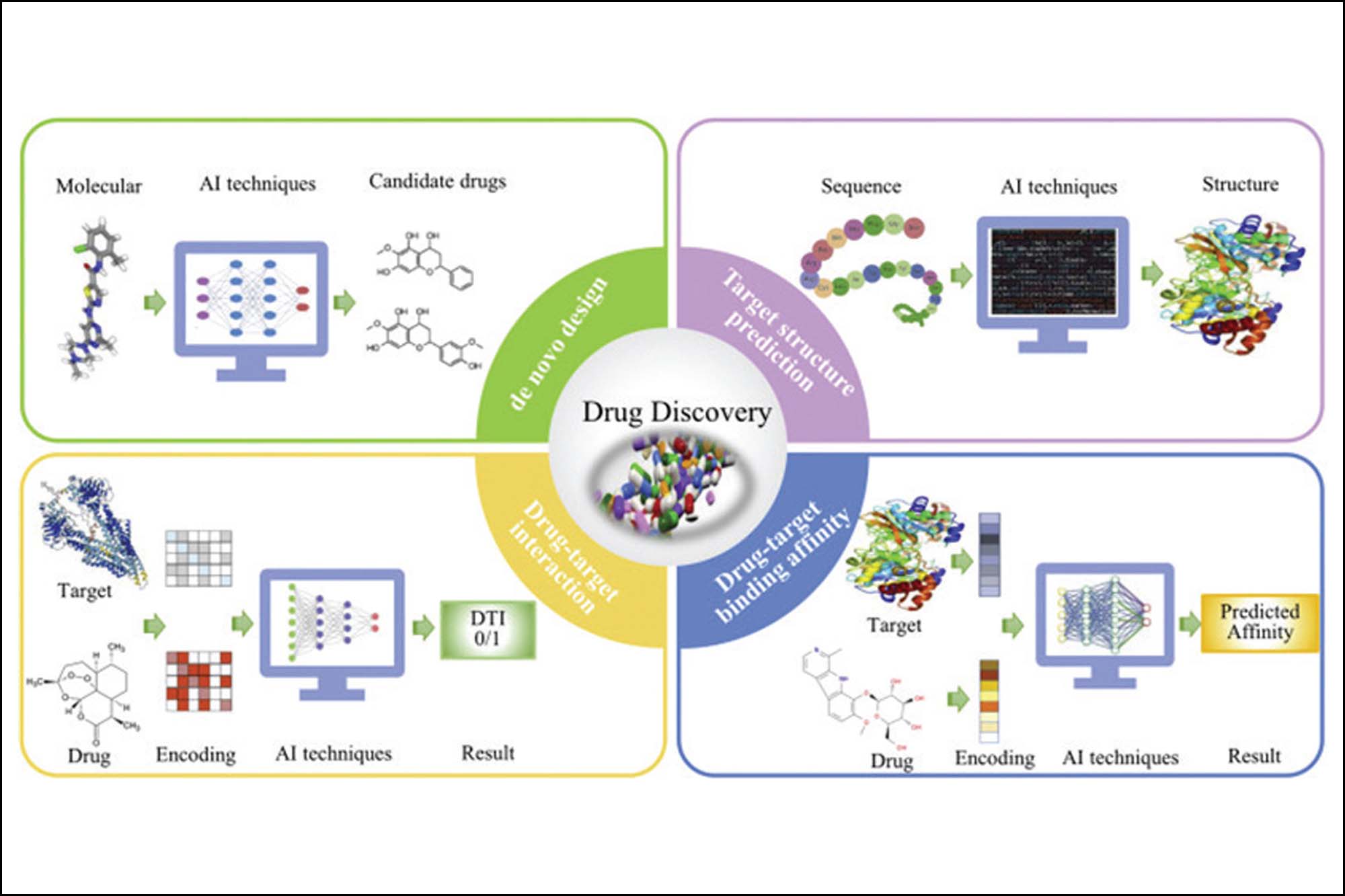
What ethical considerations need to be addressed when deploying AI in healthcare settings?
The ethical dilemma is between the Nobel cause of the healthcare industry. It is ‘saving lives and bettering life duration’ – and the commercial world can become ruthless about ‘generating money from each of these transactions’. The other issue is – Who owns the Healthcare Records – the providers, the integrators or the patients? So, personal ownership of data can be at risk of getting shared. It impacts the secrecy and sanctity of the healthcare industry.
How can AI help address the challenges of drug resistance in infectious diseases?
Drug resistance is a phenomenon of how our body elements react to the intended effect of an external drug—infectious diseases keep learning from the way they impact and how the receiver responds.
The ideal approach is to use an AI model to understand the interaction between external influences and internal learning. When it comes to infectious diseases, AI has the potential to be a game-changer in the battle against antibiotic resistance. Finally, when selecting antibiotic therapy for infections, data from local antibiotic stewardship programs are critical to ensuring that these bacteria are treated quickly and effectively.
What strategies can be employed to ensure the transparency of AI algorithms in healthcare decision-making?
The whole research world is governed by global patenting and respects the protection of ownership, so a similar model has to be built for the healthcare industry to create a neutral, non-biased, ethical system that keeps mankind at the centre. Transparency in AI systems within healthcare is also pivotal in eliminating bias and ensuring equitable care. Clinicians require assurance that AI technologies are rigorously evaluated in their specific care settings and trained on diverse data sets that genuinely reflect their patient populations.
What are the key factors hindering the adoption of AI in pharmaceutical research and development?
Barriers to AI adoption in decision-making include – human social dynamics, restrictive regulations, creative work environments, lack of trust and transparency, dynamic business environments, loss of power and control and ethical considerations.
Are AI and robotics together transforming the healthcare space?
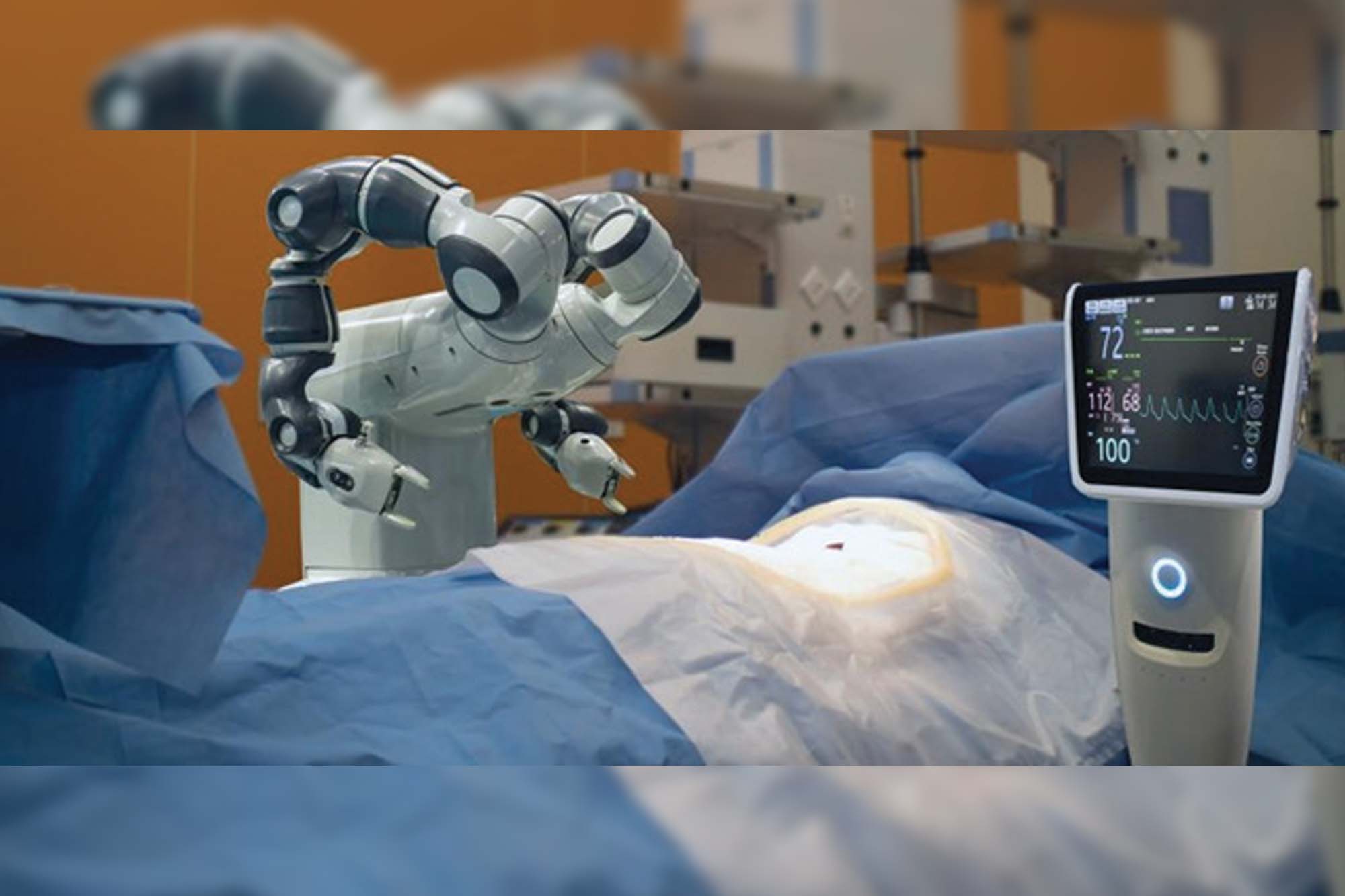
Robots have been used in medicine for more than 30 years. They range from simple laboratory robots to highly complex surgical robots that can either aid a human surgeon or execute operations themselves. In addition to surgery, they are used in hospitals and labs for repetitive tasks, rehabilitation, physical therapy, and supporting those with long-term conditions. Robots have the potential to revolutionise end-of-life care, helping people to remain independent for longer and reducing the need for hospitalisation and care homes. AI combined with the advancements in humanoid design enables robots to go even further and have ‘conversations’ and other social interactions with people to keep ageing minds sharp.

Summary
AI systems will not replace human clinicians on a large scale but will augment their efforts to care for patients. Healthcare is one of the most critical sectors in the broader landscape of big data because of its fundamental role in a productive, thriving society. AI in healthcare can enhance preventive care and quality of life and produce more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans, leading to better patient outcomes. AI can also predict and track the spread of infectious diseases by analysing data from government, healthcare, and other sources. As a result, AI can play a crucial role in global public health as a tool for combating epidemics and pandemics.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.